Code Execution Node
What is a Code Execution Node?
The Code Execution Node is a powerful tool that allows you to write and execute custom code snippets within your workflow. Through this node, you can use programming languages (currently supporting PHP and Python) to process data, perform calculations, or implement complex logic that cannot be directly achieved by other nodes. It's like embedding a small programming environment in your workflow, giving you the flexibility to address various special requirements.
Image Description:
The Code Execution Node interface consists of three main parts: the input area at the top, the code editing area in the middle, and the output configuration area at the bottom. In the code editing area, you can directly write code; at the top and bottom, you can set the input parameters needed by your code and the output parameters generated. 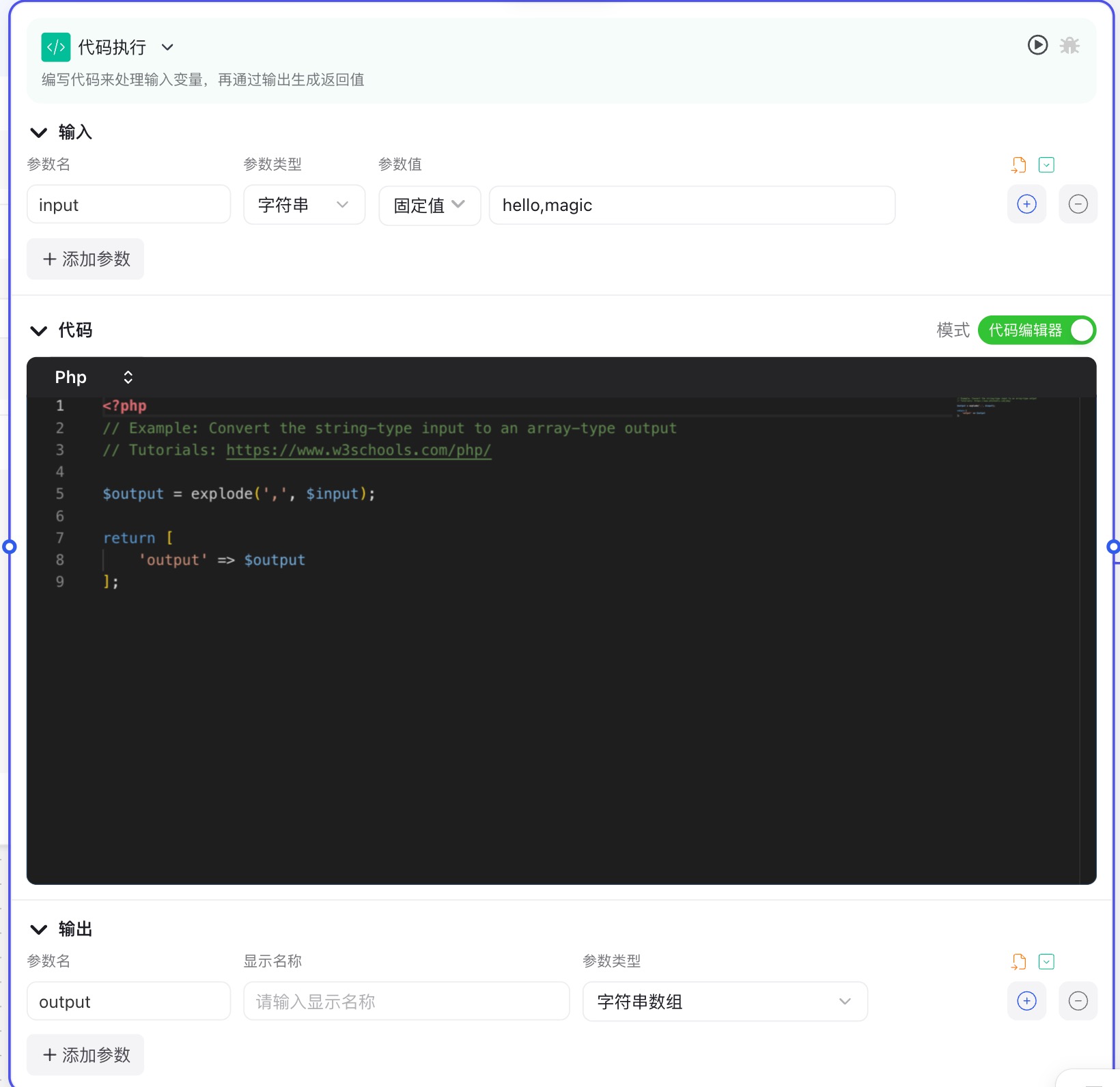
Why do you need a Code Execution Node?
When building workflows, you might encounter these situations:
- Complex Data Processing: Need to perform complex transformations, calculations, or structural adjustments to data
- Conditional Logic: Need to implement more complex conditional judgments than simple branch nodes
- Custom Functionality: Need to implement specific functions that other nodes cannot directly provide
- Special Algorithms: Need to apply specific business algorithms or formulas
The Code Execution Node is designed to solve these situations. It frees you from the limitations of preset functions, allowing you to implement fully customized logic through programming.
Application Scenarios
1. Data Format Conversion
When you need to convert data obtained from an API into a specific format, or combine data from multiple sources into a unified structure, the Code Execution Node can easily handle these conversions.
2. Complex Calculations
For scenarios involving multi-step calculations, requiring loop processing, or using specific algorithms, the Code Execution Node can implement computational logic of any complexity.
3. Custom Rule Judgment
When business rules are complex and cannot be expressed with simple condition nodes, the Code Execution Node can implement complex judgment logic with multiple conditions and multiple levels.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Language | Select the execution language for the code, supporting PHP and Python | Yes | PHP |
| Code Mode | Select the source mode for the code, can be direct writing or importing variables | Yes | Direct Writing |
| Code Content | The code snippet to be executed | Yes | Empty |
| Import Code | When "Import Variable" mode is selected, specify the variable containing the code | Only required for import mode | None |
| Input Parameters | The Code Execution Node can receive data passed from upstream nodes as input. You can add and configure these parameters in the node's "Input" tab | Yes | None |
| Output Parameters | The results of code execution can be configured as output parameters, passed to downstream nodes for use. You can add and configure these parameters in the node's "Output" tab | Yes | None |
Data Type Description
Input and output parameters support multiple data types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- String Array
- Integer Array
- Boolean Array
- Object Array
- Numeric Value
- Numeric Array
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Code Execution Node: In the workflow editor, drag the "Code Execution" node onto the canvas.
- Select Code Language: Click on the node, and in the property panel on the right, select the code language (PHP or Python).
- Write Code:
- If "Direct Writing" mode is selected, input your code in the code editor
- If "Import Variable" mode is selected, select the variable containing the code
- Configure Input Parameters:
- Click the "Input" tab
- Click the "Add Parameter" button
- Set the parameter name, type, and value
- Configure Output Parameters:
- Click the "Output" tab
- Click the "Add Parameter" button
- Set the parameter name and type
- Connect Nodes: Connect upstream nodes to the Code Execution Node, and connect the Code Execution Node to downstream nodes.
- Save Workflow: Click the save button to save your configuration.
Advanced Techniques
PHP Code Example
In PHP mode, your code will receive input parameters as variables and provide output by returning an array:
<?php
// Get input parameters
$name = $name ?? 'Guest';
$age = $age ?? 0;
// Process logic
$greeting = "Hello, {$name}!";
$isAdult = $age >= 18;
$message = $isAdult ? "You are an adult." : "You are a minor.";
// Return results (will become output parameters)
return [
'greeting' => $greeting,
'isAdult' => $isAdult,
'message' => $message
];Python Code Example
In Python mode, your code will receive input parameters as variables and provide output by defining global variables:
# Get input parameters
name = globals().get('name', 'Guest')
age = globals().get('age', 0)
# Process logic
greeting = f"Hello, {name}!"
is_adult = age >= 18
message = "You are an adult." if is_adult else "You are a minor."
# Set output parameters (will become global variables)
globals()['greeting'] = greeting
globals()['is_adult'] = is_adult
globals()['message'] = messagePrecautions
Code Safety Limitations
- Execution Time Limit: Code execution has time limits; long-running code may be interrupted.
- Resource Limitations: The execution environment has limited memory and processing capabilities; please avoid overly complex or resource-intensive operations.
- Access Restrictions: For security considerations, the code execution environment cannot directly access the file system or make network requests.
Debugging Tips
- Output Debug Information: Use
echoin PHP orprintin Python to output debug information, which will be displayed in the node's execution log. - Step-by-Step Testing: Complex logic should be broken down into small steps, tested step by step to ensure each part is correct.
- Data Validation: Add checks at the beginning of your code to verify the existence and correctness of input parameters.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why isn't my code executing correctly?
- Check for Syntax Errors: Ensure your code has no syntax errors, such as missing semicolons, unmatched brackets, etc.
- Check Variable Names: Ensure that the input parameter names referenced in the code match exactly with the configured input parameter names, including case sensitivity.
- Check Return Format: Ensure PHP code correctly returns an array, or Python code correctly sets global variables.
How to use upstream node results in code?
- Configure Input Parameters: First add parameters corresponding to upstream node results in the "Input" tab.
- Reference Variable Values: Set the parameter value to the output variable of the upstream node.
- Use in Code: Directly reference these input parameters by variable name in your code.
Best Practices
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Conditional Branch Node | The Code Execution Node can handle complex logic and then pass the results to the Conditional Branch Node for judgment. |
| HTTP Request Node | Process data returned from API requests, perform format conversion or extract key information. |
| Large Model Call Node | Process content generated by large models, such as extracting specific information, formatting, or classification. |