Vector Search Node
What is a Vector Search Node?
The Vector Search Node is a functional node in Magic Flow workflows used for quickly retrieving similar content from vector databases. It can find semantically similar content fragments from pre-stored knowledge bases based on user-provided query text. Simply put, vector search is like an intelligent search engine that not only finds content containing keywords but also understands the semantics of questions and returns relevant information.
Image Description:
The vector search node interface displays the main configuration areas of the node, including knowledge base selection, query text input, similarity threshold settings, and result quantity limits. 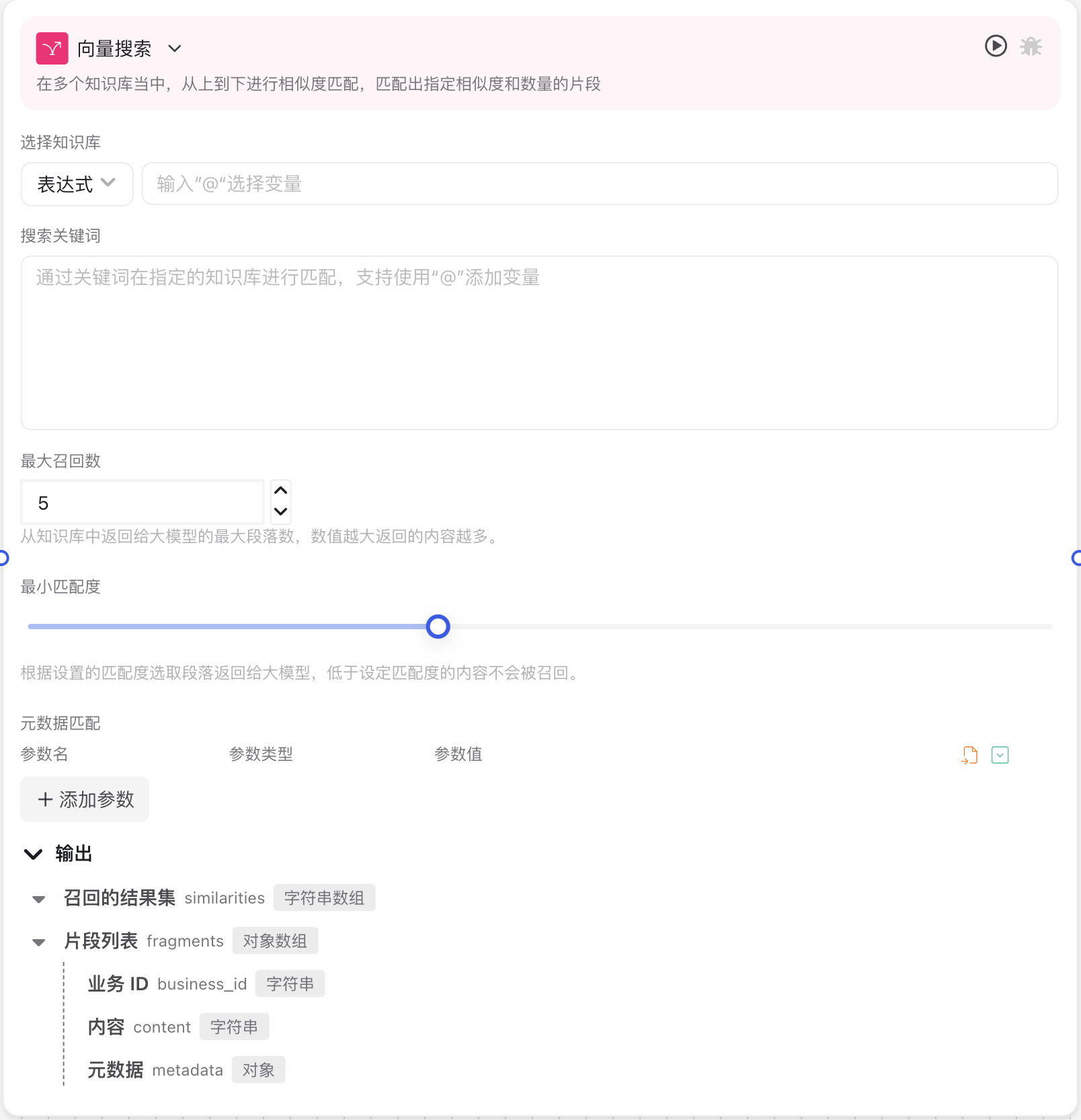
Why Do We Need a Vector Search Node?
In building intelligent applications, the vector search node solves the challenge of accurately finding relevant information from large amounts of unstructured data:
- Semantic Understanding: Based on semantics rather than simple keyword matching, able to understand the true intent of user questions
- Information Retrieval: Quickly find the most relevant content fragments from massive documents and knowledge bases
- Knowledge Support: Provide accurate professional knowledge and background information for large models, improving answer quality
- Custom Knowledge: Use enterprise-specific data to build exclusive Q&A capabilities, solving the problem of limited knowledge in general models
- Efficient Processing: Reduce the amount of information processed by large models, improve response speed, and save token consumption
Application Scenarios
1. Enterprise Knowledge Base Q&A System
Build Q&A systems based on internal company documents, product manuals, or technical materials. Employees can get precise answers using natural language questions without browsing through numerous files.
2. Intelligent Customer Service Assistant
Provide product information, common problem solutions, and other knowledge support for customer service assistants, helping customer service staff or chatbots quickly and accurately answer customer questions.
3. Document Analysis and Information Extraction
Extract specific information from large amounts of documents, such as contract terms, technical specifications, or key data from research reports, saving manual search time.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Select Knowledge Base | Choose the knowledge base to operate on, through [Fixed Value or Expression], select from knowledge bases already created in the system | Yes | None |
| Search Keywords | Text used to search for similar content, usually questions or key descriptions | Yes | None |
| Maximum Recall Count | Upper limit on the number of similar content to return | No | 5 |
| Minimum Match Score | Minimum requirement for content similarity, range 0-1, higher values mean stricter requirements | No | 0.4 |
| Metadata Matching | Filter based on document metadata information, such as document source, creation time, etc. | No | - |
Output Content
| Output Field | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Recall Result Set (similarities) | Array of similar content found in search, containing all matching text fragments | String Array |
| Fragment List (fragments) | Complete search result information, containing content, metadata, and business ID details | Object Array |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Select Knowledge Base:
- Choose different methods from the dropdown menu
- Dynamically reference knowledge bases from previous nodes or already created knowledge bases using @
- Configure Keywords:
- Input fixed search text
- Or use variable references for dynamic content, such as
to reference actual user questions
- Set Maximum Recall Count:
- Set the upper limit on the number of results to return based on needs
- Generally recommended 5-10 items, too many may introduce irrelevant information, too few may miss important content
- Adjust Match Score Threshold:
- Set similarity threshold to control result precision
- Higher threshold means more precise results but may miss relevant content
- Lower threshold means broader coverage but may include less relevant content
- Configure Metadata Filtering (Optional):
- If further result filtering is needed, set metadata filter conditions
- For example, limit documents from specific sources or time ranges
Advanced Techniques
Optimizing Search Text
The key to improving vector search effectiveness is writing effective query text:
- Be Specific and Clear: Use clear, specific descriptions rather than vague expressions
- Prioritize Key Information: Place most important keywords and concepts at the beginning of query text
- Avoid Irrelevant Information: Streamline query text, remove words that don't help the search
Collaboration with Other Nodes
Vector search node typically needs to be used in combination with other nodes:
- With Large Model Call Node:
- Use vector search results as context for the large model
- Use code execution node to process search results before passing to large model
- With Condition Branch Node:
- Check if search results are empty
- Decide subsequent processing based on result count or similarity
- With Text Segmentation Node:
- First use text segmentation to process long text
- Then perform vector storage and retrieval on segmented fragments
Notes
Vector Library Preparation
Before using vector search node, vector knowledge base needs to be prepared:
- Ensure relevant knowledge documents have been created and imported
- Check vector library update status to ensure data is current
- For large knowledge bases, consider reasonable classification to improve retrieval precision
Query Text Length
Query text length affects search effectiveness:
- Too short queries may lack sufficient information for accurate matching
- Too long queries may introduce noise, diluting core keyword weights
- Recommended query text length is between 20-100 characters
Similarity Threshold Tuning
Similarity threshold needs to be adjusted based on specific application scenarios:
- General Q&A: Recommended threshold 0.4-0.6
- Professional knowledge retrieval: Can increase to 0.6-0.8 to ensure accuracy
- Exploratory search: Can decrease to 0.3-0.5 to get more related information
Common Issues
Issue 1: Search results don't match expectations. What to do?
Solution:
- Check if knowledge base contains relevant information
- Try rewriting query text using more precise descriptions
- Lower similarity threshold to get broader results
- Use metadata filtering to narrow search scope
Issue 2: How to handle empty search results?
Solution:
- Add condition branch in workflow to check result count
- Set fallback responses or default knowledge
- Lower similarity threshold to relax matching conditions
- Use more general query text to search again
Issue 3: How to optimize slow search speed?
Solution:
- Reduce number of knowledge bases to search, only select most relevant ones
- Optimize knowledge base structure, avoid overly large single libraries
- Reduce return result count limit
- Use metadata filtering to narrow search scope
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Large Model Call Node | Use search results to provide professional knowledge support for large model |
| Code Execution Node | Process and transform search results, extract key information |
| Condition Branch Node | Decide subsequent flow based on search results |
| Text Segmentation Node | Process long text, prepare for vector storage or search |
| Vector Storage Node | Work with vector search to implement knowledge base updates and retrieval |