Subprocess Node
What is a Subprocess Node?
The Subprocess Node is a powerful organizational tool that allows you to separate a portion of functional modules to form an independent process, which can then be called in the main process. Just like when writing an article, we divide content into chapters and paragraphs, the Subprocess Node helps you break down complex workflows into smaller, more manageable parts.
Image Description:
The Subprocess Node interface consists of process selection and configuration areas. The configuration area mainly includes input parameter settings and output parameter reception, where you can configure the data exchanged with the subprocess. 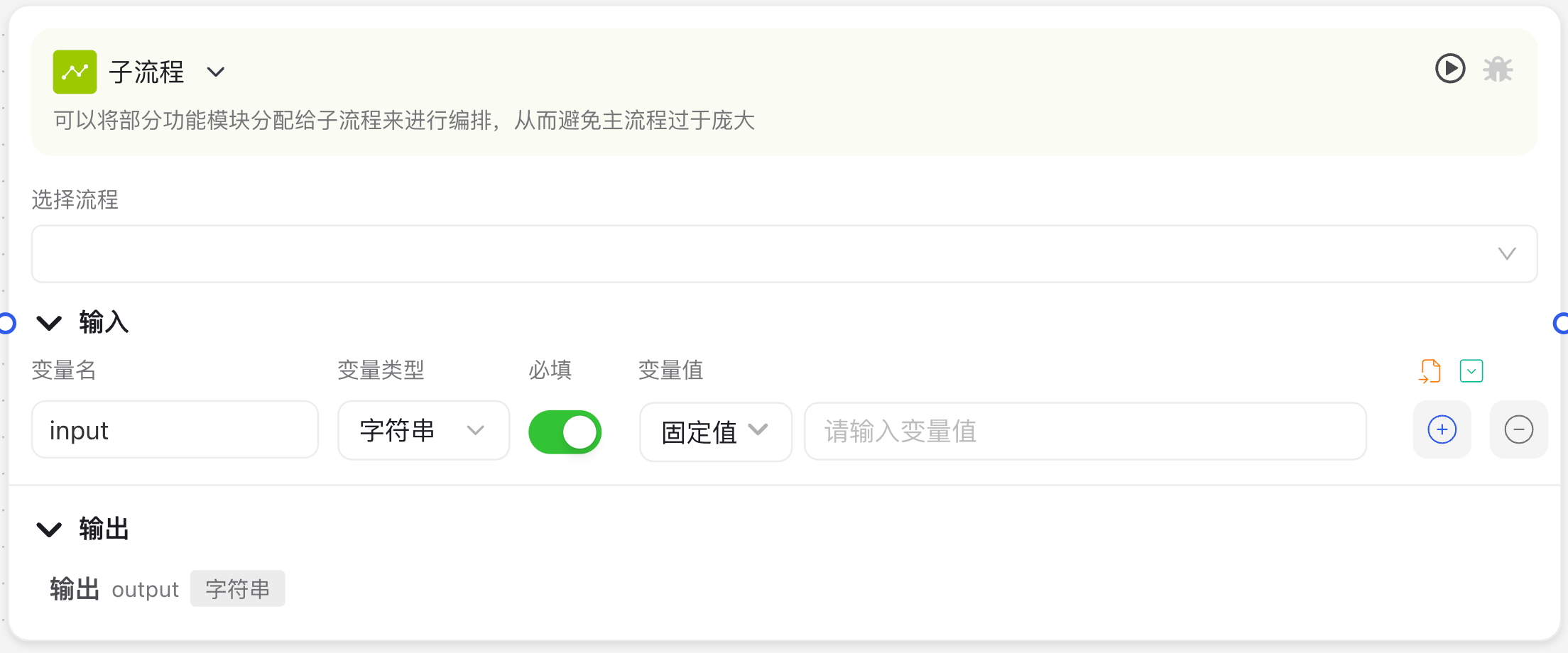
Why do you need a Subprocess Node?
When designing complex workflows, placing all functionality in a single process can make the flowchart massive and difficult to manage. The Subprocess Node can help you:
- Simplify the main process: Separate complex logic into subprocesses, making the main process clearer
- Improve reusability: A subprocess can be called by multiple different main processes
- Facilitate team collaboration: Different team members can focus on developing different subprocesses
- Enhance maintenance efficiency: When modifying a certain function, you only need to update the corresponding subprocess
Application Scenarios
Scenario 1: Modular Processing of Complex Tasks
When your AI assistant needs to perform a series of complex operations (such as multi-step data processing, multiple conditional judgments, etc.), you can break these operations down into multiple subprocesses, making the overall structure clearer.
Scenario 2: Encapsulation of Repeatedly Used Functions
For functions that need to be reused in multiple places (such as user authentication, data format conversion, etc.), you can encapsulate them as subprocesses, achieving one-time development for multiple uses.
Scenario 3: Team Collaboration in Large Projects
In large projects, different functional modules can be assigned to different team members to develop as subprocesses, and then integrated into the main process, improving team collaboration efficiency.
Node Parameter Description
The Subprocess Node mainly includes input and output parameter configurations:
Input Parameters
| Parameter Name | Parameter Description | Required | Parameter Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subprocess Name | The name of the subprocess to be called | Yes | Dropdown Selection | None |
| Input Parameters | Data passed to the subprocess after selecting it | Yes | String/Number/Boolean, etc. | None |
The Subprocess Node allows you to set multiple input parameters, each with its own name, type, and value. These parameters will be passed as initial data for the subprocess to use.
Output Parameters
| Parameter Name | Parameter Description | Parameter Type |
|---|---|---|
| Output (output) | Receives the results returned by the subprocess | String/Number/Boolean, etc. |
Output parameters are used to receive the return values after the subprocess completes execution, which you can use in subsequent nodes.
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Create a Subprocess:
- Create a new process on the Magic platform
- Configure appropriate start and end nodes
- Design the internal logic of the subprocess
- Add a Subprocess Node in the Main Process:
- Drag the Subprocess Node onto the main process canvas
- Connect preceding and subsequent nodes
- Configure the Subprocess Node:
- Select the subprocess to call from the Subprocess ID dropdown menu
- Set input parameters: Click the "+" button to add parameters, specifying parameter name, type, and value
- Set output parameters: Specify the variable name used to receive the subprocess return results
- Save and Test:
- Save the main process design
- Run the main process and check if the subprocess executes as expected
Advanced Techniques
- Parameter Transfer Optimization:
- Use variable reference method to pass parameters, dynamically inputting the output of preceding nodes
- For complex data structures, use JSON format for transfer, enhancing data exchange capabilities
- Error Handling:
- Add conditional judgment nodes within the subprocess to handle potential exceptional situations
- Return execution status through output parameters, letting the main process know whether the subprocess executed successfully
- Nested Subprocesses:
- Subprocesses can call other subprocesses, forming a multi-layer nested structure
- Be careful to control nesting depth, avoiding excessive complexity that makes maintenance difficult
Precautions
Avoid Circular Calls
Do not call the parent process within a subprocess, as this will result in infinite loop calls, eventually depleting system resources.
Parameter Type Matching
Ensure that the parameter types passed to the subprocess match the types expected by the subprocess. Type mismatches may cause subprocess execution errors.
Process Version Management
When modifying a subprocess, be aware that it may affect all main processes that call that subprocess. It is recommended to create a copy of the subprocess for testing before making significant modifications.
Resource Limitations
Subprocesses also consume system resources, and too many nested subprocesses may lead to performance degradation. It is recommended to keep nesting levels to no more than 3 layers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Unable to Retrieve Subprocess Output in the Main Process
Problem: Configured a subprocess node, but cannot retrieve the subprocess's output results in the main process. Solution:
- Check if the subprocess has correctly set output parameters for the end node
- Confirm that the output variable name in the subprocess node is configured correctly
- Verify that the subprocess completes execution normally and is not stuck at some point
Subprocess Execution Fails Without Error Messages
Problem: The subprocess does not execute as expected, but the system does not display clear error messages. Solution:
- Test the subprocess separately to see if it runs normally
- Check if input parameters are passed correctly
- Add log nodes or message reply nodes in the subprocess to output intermediate process information, helping to locate the problem
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Conditional Branch Node | Decide the subsequent process flow based on the execution results of the subprocess |
| Variable Saving Node | Save the output results of the subprocess as variables for later use |
| Large Model Call Node | Process the data returned by the subprocess to generate more intelligent responses |
| Message Reply Node | Display the results of subprocess processing to the user |