Intent Recognition Node
What is an Intent Recognition Node?
The Intent Recognition Node is an intelligent analysis node in Magic Flow workflow that can understand and analyze user input text to identify user intentions. Simply put, this node acts like an "understanding expert" that can discern what users want to do and guide the workflow to different processing paths based on different intents.
Image Description:
The Intent Recognition Node interface includes model selection and branch setting areas, where you can define multiple intent branches. Each branch includes an intent name and description, as well as different process paths corresponding to different intents. 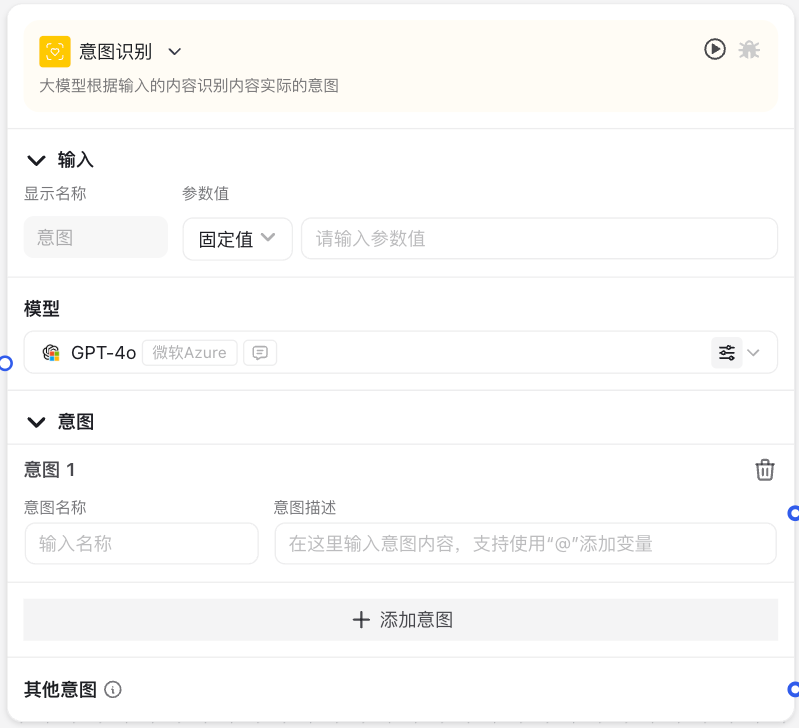
Why Do We Need Intent Recognition Node?
In building intelligent applications, the Intent Recognition Node plays a key role as "intelligent navigation":
- Automatic Classification Processing: Automatically identify user intent based on input, without requiring users to explicitly select functions
- Multi-path Process Design: Trigger different processing flows based on different intents, providing personalized experiences
- Improve User Experience: Allow users to express needs in natural language rather than following fixed commands or menus
- Reduce Manual Judgment: Automate the intent analysis process, saving human resources
- Simplify Complex Processes: Simplify complex conditional judgments into semantic-based intent recognition
Application Scenarios
1. Intelligent Customer Service Routing
Design a customer service system that can automatically determine the type of user inquiry, such as product consultation, after-sales service, complaints and suggestions, etc., and guide users to the corresponding professional processing flow.
2. Multi-functional Assistant
Build a personal assistant integrating multiple functions that can determine whether users want to check weather, set reminders, find information, or chat casually based on natural language input, and execute corresponding functions.
3. Intelligent Form Filling
Create an intelligent form assistant that can extract key information from users' natural language descriptions and automatically fill in corresponding form fields, simplifying the data entry process.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Select the large language model for intent recognition | Yes | gpt-4o-mini-global |
| Intent | User input content for intent analysis | Yes | None |
| Intent Branches | Define different intent categories and their processing flows | Yes | None |
Model Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto Load Memory | Whether to enable automatic memory function to remember dialogue history for intent recognition | No | Yes |
| Maximum Memory Count | The node will only remember n messages, where n is your set maximum memory count | No | 10 |
Intent Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Intent Name | Define a specific intent name, such as "Product Inquiry", "Refund Request", etc. | Yes |
| Intent Description | Detailed description of the intent to help the model recognize intent more accurately | No |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Choose Appropriate Model:
- For accuracy, recommend choosing advanced models like GPT-4
- For simple intent recognition tasks, faster models like GPT-3.5 can also be used
- Set Intent Input:
- Reference user input message in the "Intent" parameter, typically using variables like
- Ensure input contains sufficient information for model analysis
- Reference user input message in the "Intent" parameter, typically using variables like
- Define Intent Branches:
- Click "Add Branch" button to create multiple intent branches
- Set clear intent names and detailed descriptions for each branch
- Set at least one "else" type fallback branch for unrecognized cases
- Configure Branch Destinations:
- Set destination nodes for each intent branch when that intent is recognized
- Ensure all possible intents have corresponding processing paths
- Adjust Advanced Parameters (optional):
- Adjust temperature, auto memory, etc. parameters as needed
- For scenarios requiring high accuracy, set temperature lower (e.g., 0.2)
Collaboration with Other Nodes
Intent Recognition Node typically needs to work with other nodes:
- With Wait Node:
- Use wait node to get messages after user input
- Use wait node output as intent recognition input
- With Large Model Call Node:
- Use different prompt templates based on recognized intent
- Pass intent recognition results to large model to enhance context understanding
- Complement with Conditional Branch Node:
- Use conditional branch nodes for clear rule-based judgments
- Use intent recognition nodes for fuzzy semantic understanding
Important Notes
Intent Quantity and Quality
Intent quantity affects recognition accuracy and efficiency:
- Too many intents may lead to confusion and misidentification
- Recommend controlling to 5-10 intents per node, ensuring clear distinctions between intents
- For complex systems, consider using multi-level intent recognition, like recognizing main categories first, then subcategories
Default Branch Setting
Always ensure setting an "else" type default branch:
- As a fallback path when no predefined intent is recognized
- Can guide users to clarify intent or provide more information
- Prevent process interruption due to unrecognizable intent
Performance Considerations
Intent recognition process may consume computational resources:
- Complex intent systems may increase recognition time
- For scenarios requiring real-time response, consider simplifying intent descriptions
- Consider using faster models or optimizing prompt structures
Common Issues
Issue 1: How to Improve Intent Recognition Accuracy?
Solutions: Key factors for improving accuracy:
- Provide detailed intent descriptions and diverse examples
- Ensure sufficient distinction between different intents
- Use more advanced models (e.g., GPT-4 instead of GPT-3.5)
- Lower temperature parameter (e.g., 0.2-0.3) to increase certainty
- Consider enabling memory function to utilize conversation history for context
Issue 2: What If Intent Recognition Always Goes to Default Branch?
Solutions: Possible causes and solutions:
- Check if intent descriptions are clear and detailed enough
- Confirm if user input contains sufficient information indicating intent
- Check for overlapping intents causing confusion
- Try adding common expressions to intent descriptions
- Use debugging features to check model recognition process and confidence
Issue 3: How to Handle Multiple Intents?
Solutions: When user input may contain multiple intents:
- Design branch priorities to let model recognize main intent
- Consider setting mixed intent branches for common intent combinations
- Add clarification steps in process to confirm primary intent
- Use chain processing to handle main intent first, then secondary intents
Best Practices
Common Paired Nodes
| Node Type | Pairing Reason |
|---|---|
| Wait Node | Get user input as source for intent recognition |
| Large Model Call Node | Generate corresponding responses based on recognized intent |
| Conditional Branch Node | Handle simple rule-based judgments |
| Message Reply Node | Give feedback to users about recognition results or request clarification |
| Subprocess Node | Execute independent processing flows for each intent |