Large Model Call Node
What is a Large Model Call Node?
The Large Model Call Node is a core node in Magic Flow workflow that allows you to interact directly with large language models (such as GPT-4) for generating text content, answering questions, analyzing content, or performing reasoning. Simply put, this node acts as a bridge for you to communicate with artificial intelligence on the Magic platform.
Image Description:
The Large Model Call Node interface includes core configuration areas such as model selection, system prompts, user prompts, as well as advanced configuration options like model parameter adjustment and knowledge base configuration. 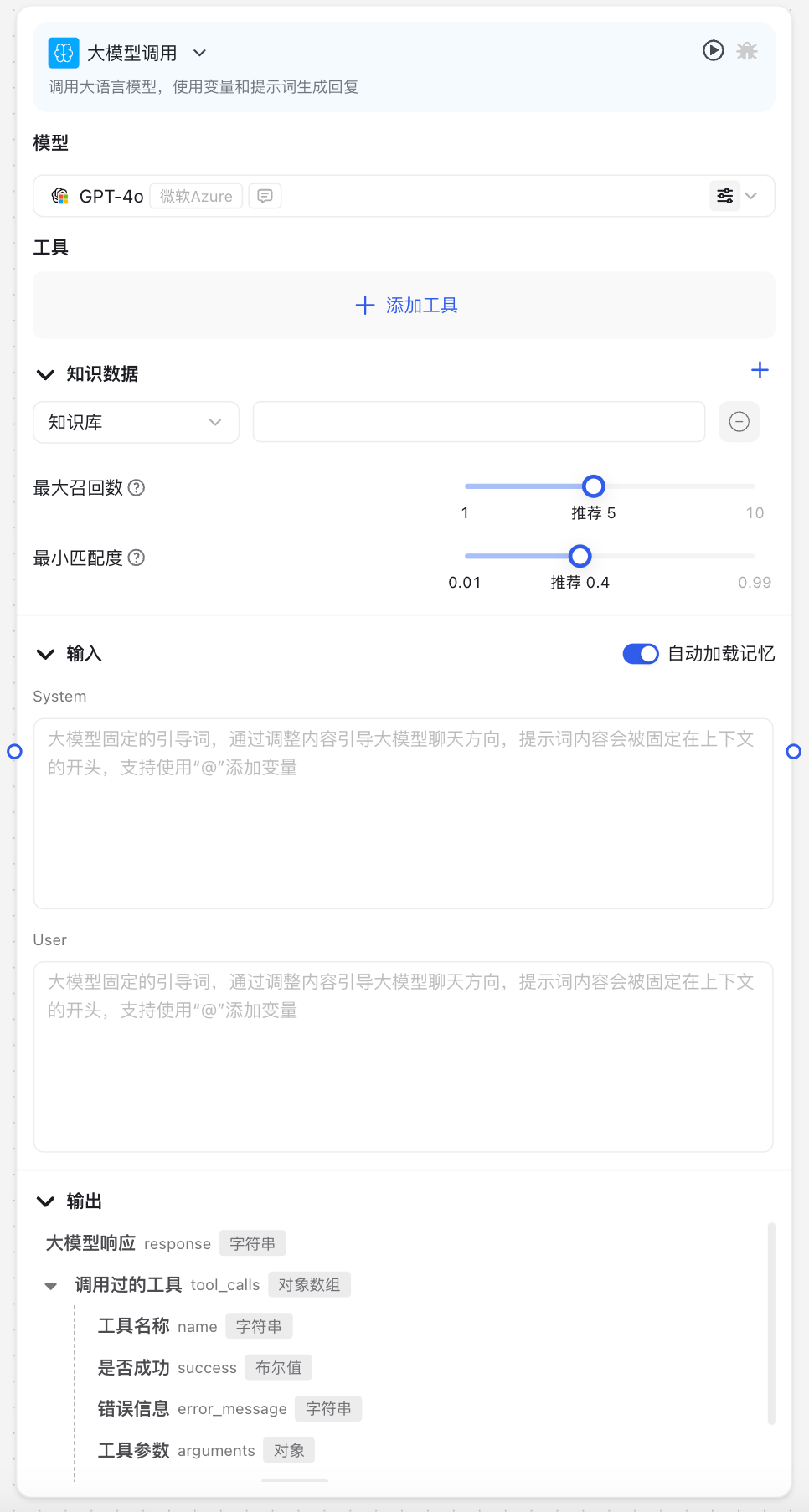
Why Do We Need Large Model Call Node?
In the process of building intelligent applications, the Large Model Call Node acts as the "brain", providing intelligent decision-making and content generation capabilities for your workflow:
- Natural Language Processing: Understand and generate human language, enabling applications to communicate naturally with users
- Content Creation: Generate copy, summaries, translations, or other creative content
- Knowledge Q&A: Answer professional domain questions based on configured knowledge bases
- Logical Reasoning: Analyze information and draw conclusions to assist decision making
- Personalized Interaction: Provide customized responses based on user needs and history
Application Scenarios
1. Intelligent Customer Service Bot
Design a customer service bot that can answer product inquiries and solve user problems by configuring professional knowledge bases to provide accurate product information and solutions.
2. Content Creation Assistant
Build an assistant that can generate various types of copy, summaries, or creative content, such as marketing copy, product descriptions, or social media posts.
3. Knowledge Base Q&A System
Create a Q&A system based on internal company documents, allowing employees to quickly access professional information and improve work efficiency.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Transform data analysis results into easy-to-understand natural language explanations, helping non-technical personnel understand complex data.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Select the large language model to use, such as GPT-4, Claude, etc. | Yes | gpt-4o-global |
| Tools | Configure associated tool capabilities, letting model answer based on specific knowledge | ||
| Knowledge Base Settings | Configure associated knowledge bases, letting model answer based on specific knowledge | No | None |
| System Prompt | Background instructions for the model, defining its role and overall behavior | Yes | None |
| User Prompt | Specific questions or instructions from users | No | None |
Model Configuration
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Control output randomness, higher values for more creative answers, lower for more deterministic | No | 0.5 |
| Auto Load Memory | Whether to enable automatic memory function to remember conversation history | No | Yes |
| Maximum Memory Count | Maximum number of historical messages to remember | No | 50 |
| Visual Understanding Model | Large model name for processing images | No | None |
| Historical Messages | Set historical conversation messages for building dialogue context | No | None |
Output Content
| Output Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Model Response (response) | Model's reply content, can be displayed to users or passed to downstream nodes |
| Tool Calls (tool_calls) | Information about tools called by the model, including tool names, parameters, results, etc. |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Choose Appropriate Model:
- Select corresponding large language model based on needs
- Choose regular models for general tasks, advanced models like GPT-4 for complex tasks
- Write System Prompt:
- Clearly define model's role, like "you are a customer service representative"
- Set answer style and scope
- Inform model about available resources or tools
- Configure User Prompt:
- Can directly input fixed questions or instructions
- Can also use variables to reference dynamic content, like
to reference actual user input
- Set Model Parameters:
- Adjust temperature to control answer creativity or accuracy
- Set whether to enable automatic memory and history count
- Configure Knowledge Base (Optional):
- Select knowledge bases to associate
- Set similarity threshold and search result count
Advanced Tips
Prompt Optimization
Writing high-quality prompts is key to effectively using large models:
- Be Specific: Clearly express your expectations and requirements
- Role Setting: Give model clear role positioning in system prompt
- Step Breakdown: Guide model to think through complex problems step by step
Collaboration with Other Nodes
- Pair with Message Reply Node:
- Display model output to users through message reply node
- Set user prompt empty, let user messages automatically serve as input
- Combine with Conditional Branch Node:
- Use intent recognition node to analyze user intent
- Route to different processing flows based on different intents
- Work with Knowledge Retrieval Node:
- First use knowledge retrieval to get relevant information
- Then provide retrieval results as context to large model
Important Notes
Token Limits
Each model has maximum token processing limits, exceeding will cause errors:
- GPT-3.5: Maximum 16K tokens
- GPT-4: Maximum 128K tokens
- Claude: Maximum 200K tokens
Knowledge Timeliness
Large models have training cutoff dates and may not know latest information, recommend:
- For scenarios requiring latest information, consider combining with HTTP request node to get real-time data
- Or regularly update latest information through knowledge base
Sensitive Information Handling
Large models may process user-provided information, note:
- Avoid including confidential or sensitive information in prompts
- For data requiring confidentiality, recommend using knowledge base rather than direct input
Common Issues
Issue 1: What If Model Replies Don't Meet Expectations?
Solutions: Prompts might not be clear enough. Try:
- Modify system prompt to more specifically define task and expectations
- Add examples showing ideal Q&A patterns
- Adjust temperature parameter, lower it for more deterministic answers
Issue 2: How to Handle Professional Questions Model Can't Answer?
Solutions: Large models rely on training data, may have limited knowledge in specific domains:
- Configure professional knowledge base to provide domain knowledge support
- Add necessary background knowledge in system prompt
- Use instruction "explicitly state if information not found" to avoid making up answers
Issue 3: What If Large Model Call Node Executes Slowly?
Solutions: Multiple factors affect speed:
- Try using faster responding models (e.g., GPT-3.5 instead of GPT-4)
- Reduce historical message count to lower processing burden
- Optimize prompts to make instructions more concise and clear
Best Practices
Common Paired Nodes
| Node Type | Pairing Reason |
|---|---|
| Message Reply Node | Send model-generated content to users |
| Conditional Branch Node | Decide next operation based on model output |
| Knowledge Retrieval Node | Provide professional domain knowledge support |
| Historical Message Query | Provide conversation context, enhance coherence |
| Variable Save Node | Save important information for subsequent processes |