End Node
What is an End Node?
The End Node is the final node in a workflow, used to return the results after workflow execution. Each workflow requires at least one end node, but can have multiple end nodes corresponding to different ending paths.
Image Description:
The end node interface mainly contains the "Output" configuration area, where you can define parameters that need to be returned when the workflow ends. The interface supports adding multiple output parameters, each requiring parameter name, display name, and parameter value settings. Parameter values can be expressions or fixed values, supporting references to data generated by other nodes in the workflow. 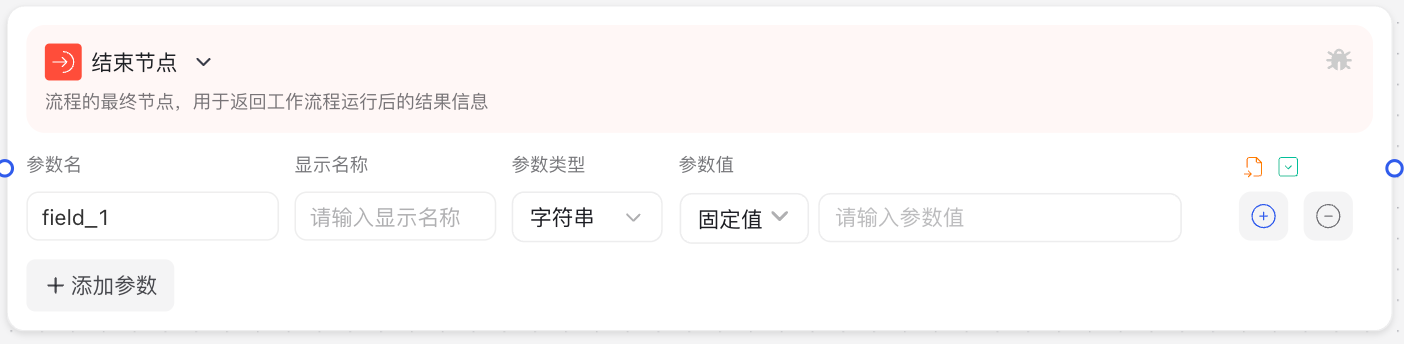
Why Do We Need an End Node?
When building workflows, the end node solves the following key problems:
- Clarify Workflow Endpoint: The end node clearly marks the termination point of workflow execution, making the entire process logic clearer.
- Define Output Results: The end node can configure output parameters to determine which result data the workflow ultimately presents externally.
- Standardize Data Return: The end node formats and organizes output data to ensure consistency and usability of returned results.
- Support Complex Flows: In complex workflows with multiple possible endpoints, different end nodes can return different result data.
Application Scenarios
1. Intelligent Q&A Flow
In Q&A-type AI assistants, the end node can output the final processed answer content, along with possible related recommendations or reference materials.
2. Data Processing Workflow
In data analysis or processing flows, the end node returns processed data results, such as statistical reports, analysis conclusions, etc.
3. Subprocess Calls
When called as a subprocess by the main workflow, the end node defines the data that the subprocess needs to return to the main workflow, similar to function return values.
Node Parameter Description
Output Parameters
The core configuration of the end node is output parameters, where you can define the data that needs to be returned when the workflow ends:
| Configuration Item | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter Name | Identifier for output parameter, used to reference this parameter in the system | Yes |
| Display Name | Friendly display name for the parameter, used for interface display | Yes |
| Parameter Type | Supports setting different parameter types, such as: string, array, etc. | Yes |
| Parameter Value | Actual value of the parameter, can be fixed value, expression, or variable reference | Yes |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add End Node:
- Drag "End Node" from the node panel to the canvas
- Connect the output of the previous node to the end node
- Configure Output Parameters:
- Click "Add Parameter" button to add parameters that need to be output
- Set parameter name (e.g., "result") and display name (e.g., "Processing Result")
- Select parameter value type (expression or fixed value)
- If choosing expression, use
${variable_name}to reference variables in the workflow
- Save Configuration:
- Confirm all necessary output parameters have been configured
- Save node configuration to complete end node setup
Advanced Techniques
Multi-parameter Organization
When needing to return multiple related parameters, you can use the following organization methods:
- Related Parameter Grouping: Organize parameters by function or data type to make structure clearer
- Use Nested Structure: Use JSON format to organize complex data, such as
{"data": ${result}, "meta": ${metadata}} - Parameter Naming Convention: Use unified naming rules, such as
result_main,result_details, etc.
Dynamic Output Processing
Return different results based on different process paths:
- Conditional Judgment Preprocessing: Use condition branch node before end node to connect to different end nodes based on different conditions
- Variable Packaging: Use code execution node to pre-package multiple possible results into a variable, then reference in end node
Notes
Parameter Naming Convention
- Avoid Special Characters: Parameter names should use letters, numbers, and underscores, avoid spaces and special characters
- Semantic Naming: Parameter names should reflect their content and purpose, such as
search_resultrather than simpledata - Maintain Consistency: Multiple end nodes in the same workflow should follow unified naming conventions
Data Type Handling
- Type Consistency: Ensure output parameter data types meet caller's expectations
- Format Conversion: Use code execution node for data format conversion when necessary
- Null Value Handling: Consider cases where parameters may be null, provide reasonable default values
Multi-end Node Management
- Clear Identification: Add clear labels or comments to different end nodes
- Path Planning: Ensure each possible execution path has a corresponding end node
- Result Consistency: Even for different end nodes, maintain consistency in key parameter structure
Common Issues
Why aren't my set output parameters showing in the results?
- Check Parameter Names: Confirm parameter names are spelled correctly
- Check Expressions: If using expressions, confirm syntax is correct and referenced variables exist
- Check Process Execution: Confirm workflow actually executed to this end node
- Check Variable Scope: Confirm referenced variables are accessible within end node's scope
How to return complex data structures?
- Use JSON Format: Use JSON format in expressions to organize complex data, such as
{"items": ${list}, "count": ${count}} - Preprocess Data: Use code execution node before end node to build complex data structures
- Structured Naming: Use hierarchical parameter naming, such as
result_header,result_body,result_footer
How to ensure each path in a workflow with multiple paths has appropriate ending?
- Path Analysis: Sort out all possible execution paths in the workflow
- Corresponding End Nodes: Set independent end nodes for each main path
- Unified Return Structure: Maintain consistent core parameter structure across all end nodes
- Status Identification: Include status identifiers (such as
status,code) in output to facilitate identifying results from different paths
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Condition Branch Node | Connect to different end nodes based on different conditions, return different results |
| Code Execution Node | Organize and format final output data before ending |
| Large Model Call Node | Generate structured answer content, then return through end node |
| Message Reply Node | Send message to user before ending, end node then records operation result |