Selector Node
What is a Selector Node?
The Selector Node is a conditional judgment node in the Magic Flow workflow that allows you to divide the workflow into different execution paths based on set conditions. It's like a fork in the road, choosing different directions based on different situations. Through the Selector Node, you can build intelligent workflows with logical branches, implementing functions that perform different operations based on different conditions.
Image Description:
The Selector Node interface shows the condition setting area, including reference variables, selection conditions (such as equals, conditions, etc.), and comparison value (expression or fixed value) configuration. The interface supports combining multiple conditions through "OR" and "AND" buttons to implement complex judgment logic. 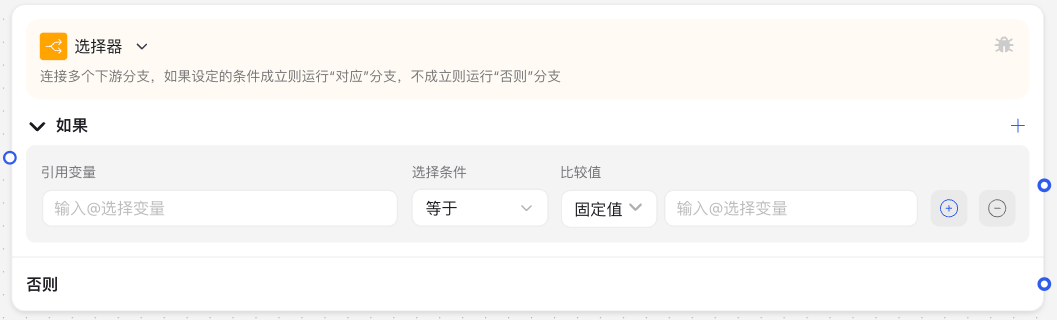
Why do you need a Selector Node?
When building intelligent workflows, the Selector Node plays the role of a "decision maker," providing your application with conditional judgment and path selection capabilities:
- Logical Branch Processing: Choose different processing paths based on different conditions
- Multi-scenario Adaptation: Execute different operations for different user inputs or data states
- Business Rule Implementation: Transform business rules into executable conditional judgments
- Error Handling: Choose normal flow or exception handling based on operation results
- Personalized Process: Provide customized experiences based on user characteristics or historical behavior
Application Scenarios
1. User Classification Guidance
Guide users to different service processes based on information provided by users (such as age, occupation, needs, etc.), providing targeted assistance.
2. Approval Process
Decide whether higher-level approval is needed or direct approval based on application amount, applicant level, and other conditions.
3. Intelligent Q&A System
Analyze user question types and direct them to corresponding professional answer processes based on different question categories.
4. Data Processing Flow
Choose different subsequent processing methods based on data quality, data characteristics, or processing results.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Variable | Select the variable to be judged | Yes | None |
| Selection Condition | Set comparison method, such as equals, conditions, etc. | Yes | Equals |
| Comparison Value | Set the target value for comparison, can be an expression or fixed value | Yes | None |
| Condition Combination Logic | Relationship between multiple conditions, can be "AND" or "OR" | No | AND |
Condition Type Description
| Condition Type | Description | Applicable Data Types |
|---|---|---|
| Equals | Judge whether the variable value is exactly the same as the set value | Text, Number, Boolean |
| Condition | Use complex conditional expressions for judgment | All types |
| Fixed Value | Compare with a specific fixed value | Text, Number, Boolean |
| Expression | Compare using the results of expression calculation | Text, Number, Object |
Output Content
The Selector Node does not have specific output content but chooses different execution paths based on the condition judgment result:
- When conditions are met: Execute the "Corresponding" branch
- When conditions are not met: Execute the "Otherwise" branch
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Select Judgment Variable:
- Select the variable to be judged from the dropdown menu
- Can be user input, output from upstream nodes, or global variables
- Set Judgment Conditions:
- Select the appropriate condition type (equals, conditions, etc.)
- Set the corresponding comparison value based on the condition type
- Configure Multiple Conditions (Optional):
- Click the "+" button to add additional conditions
- Use the "AND" button to require all conditions to be met simultaneously
- Use the "OR" button to require only one condition to be met
- Connect Downstream Nodes:
- Connect the "Corresponding" output to the node to be executed when the condition is met
- Connect the "Otherwise" output to the node to be executed when the condition is not met
Collaboration with Other Nodes
The Selector Node typically needs to be used in combination with other nodes:
- Pair with Variable Saving Node:
- Use the Variable Saving Node before the Selector to record information needed for judgment
- Save the result state again after the Selector judgment
- Combine with Large Model Call Node:
- Use the large model to generate content or analysis
- The Selector decides on subsequent processing based on the analysis results
- Coordinate with Data Processing Node:
- Preprocess and check data
- The Selector chooses processing methods based on data characteristics
Precautions
Variable Type Matching
Ensure that the judgment variable type matches the comparison value type to avoid unexpected results:
- Number compared with number (e.g.,
5 > 3) - Text compared with text (e.g.,
"hello" == "hello") - Boolean compared with boolean (e.g.,
true == false)
Condition Priority
When using multiple conditions, pay attention to the priority of condition combinations:
- "AND" has higher priority than "OR"
- For complex conditions, it is recommended to use expressions to clarify priority
Path Processing
Ensure that all possible condition branches have corresponding processing flows:
- Avoid "dangling" paths
- Check if all possible situations are handled
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What if the condition judgment result does not match expectations?
Solution: The variable type or value may not meet expectations:
- Check the actual value and type of the variable (can use the Code Node to output variable information)
- Confirm that the comparison condition is correctly set
- For text comparison, pay attention to case and space differences
Question 2: How to handle judgment of multiple situations?
Solution: For scenarios that need to judge multiple different situations:
- Use multiple Selector Nodes in series to form a complete judgment chain
- Or use the Intent Recognition Node to classify first, then further process with the Selector
- For complex situations, consider using the Code Node for custom logic processing
Question 3: What if the Selector Node errors when judging objects or arrays?
Solution: Objects and arrays require special handling:
- Use expressions to access specific properties of objects (e.g.,
user.name) - For arrays, use expressions to check length or specific elements
- For complex object comparisons, it is recommended to first use the Code Node to convert to simple types
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Large Model Call Node | Perform conditional judgment based on results after analyzing content |
| Variable Saving Node | Record judgment results for reference in subsequent processes |
| Code Execution Node | Handle complex judgment logic or data conversion |
| Message Reply Node | Reply with different content based on different conditions |
| HTTP Request Node | Choose different processing methods based on request results |