Document Parsing Node
What is a Document Parsing Node?
The Document Parsing Node is your "entry point" for processing various files and data sources in Magic Flow. It works like an intelligent reader, capable of reading and understanding document content in different formats, converting original files into text data that subsequent nodes can process. Whether it's locally uploaded PDF, WORD files, or web content from the internet, the Document Parsing Node can help you extract valuable information.
Image Description:
The Document Parsing Node interface mainly consists of "Display Name", "Add Parameter" options, "Parameter Value", and "Expression" setting areas. Users can configure data sources, file types, and parsing methods in these parameter settings. 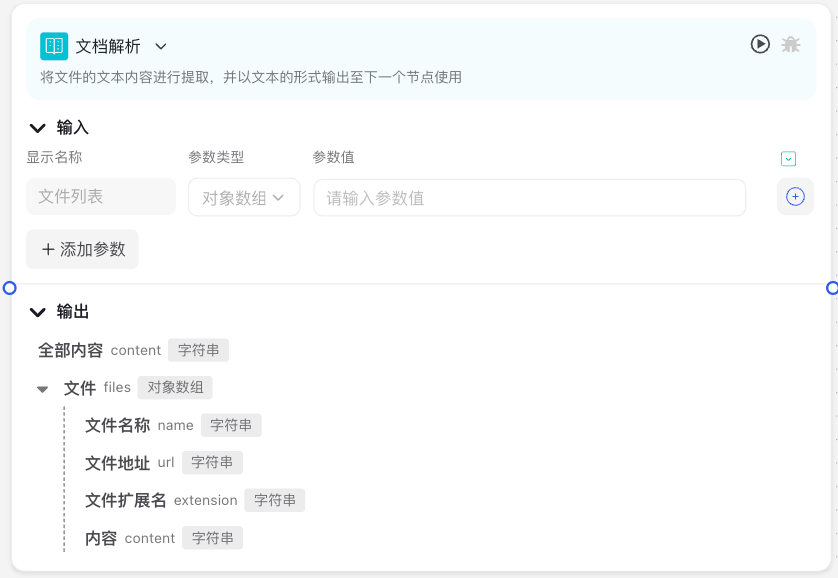
Why do you need a Document Parsing Node?
When building AI applications, we often need to process documents and data in various formats. The Document Parsing Node solves the following problems:
- Format Conversion: Converting documents in various formats (PDF, DOCX, webpages, etc.) into standard text format for easier subsequent processing
- Content Extraction: Extracting valuable text content from complex files
- Unified Entry Point: Providing a unified processing entry point for data from different sources (local files, network content, databases, etc.)
- Preprocessing: Performing preliminary cleaning and formatting of raw data to improve the quality of subsequent analysis
Through the Document Parsing Node, you can easily convert data from various sources into text form that large models can understand and process, making it an essential component for building knowledge Q&A and document analysis applications.
Application Scenarios
Scenario One: Knowledge Base Q&A System
Import and parse internal company documents, product manuals, training materials, etc., and combine them with large model nodes to build a Q&A system based on enterprise knowledge, helping employees quickly obtain the information they need.
Scenario Two: Webpage Content Analysis
Parse the content of specific webpages, extract key information for market analysis, competitor monitoring, or information compilation.
Scenario Three: Intelligent Document Processing
Batch parse documents submitted by customers (such as resumes, application forms, etc.), extract key information, and perform automated processing and classification.
Node Parameter Description
Input Parameters
The Document Parsing Node has the following main input parameters:
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| File List | List of files to be parsed, which can be locally uploaded files, network URLs, or variable references | Yes | None |
Output Variables
The Document Parsing Node outputs the following variables, which can be used in subsequent nodes:
| Variable Name | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Full Content (content) | Parsed text content | "This is a product manual, including the following features..." |
| File (file_info) | Basic information about the file, including file name, file address, content, type, etc. |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Document Parsing Node
- Configure File Source
- Select "File Upload" to upload local files
- Select "Network URL" to input webpage addresses
- Select "Variable" to use file data output from previous nodes
- Connect Downstream Nodes Connect the output of the Document Parsing Node to subsequent processing nodes, such as Text Segmentation Node, Large Model Call Node, etc.
Advanced Techniques
- Batch File Processing
- Dynamic URL Parsing
- Combine with Loop Nodes
- Conditional Parsing
Precautions
File Size Limitations
The Magic Flow platform has size limitations for uploaded files, typically not exceeding 50MB. For larger files, it is recommended to split them before uploading or to introduce them using the URL method.
File Format Support
Although the Document Parsing Node supports multiple formats, parsing effects may vary for different formats:
- PDF documents: Support text extraction and table recognition
- Word documents: Support complete text and format extraction
- Web content: Support HTML parsing, but complex JavaScript-rendered content may not be fully obtained
- Image files: Need to extract text through OCR, accuracy affected by image quality
Network Resource Access
When parsing network content via URL, please ensure:
- The URL is publicly accessible
- The content does not require login verification
- The resource does not violate copyright and legal regulations
Performance Considerations
Parsing large documents or complex formats may take longer. It is recommended to:
- Set appropriate timeout periods
- Preprocess or split large documents
- Avoid parsing too many files in one workflow
Frequently Asked Questions
Question One: Document Parsing Fails or Content is Missing
Possible Causes: Incompatible file format, damaged or encrypted file, OCR recognition failure Solutions:
- Check if the file can be opened normally
- Try converting the file to a more common format (such as PDF to TXT)
- For encrypted documents, remove encryption before uploading
- Improve image quality or adjust OCR parameters
Question Two: Parsing Takes Too Long
Possible Causes: File is too large, complex format, slow network resource loading Solutions:
- Split large documents into multiple smaller files
- Increase timeout settings
- For network resources, download locally first then upload for parsing
- Simplify processing workflow, only extract necessary content
Question Three: Special Formats Cannot Be Parsed
Possible Causes: Non-standard format, new version format, professional software format Solutions:
- Convert the file to a standard format before uploading
- Use professional software to export to a compatible format
- Combine with code nodes for custom parsing logic
- Contact platform support team for technical assistance
Common Node Combinations
The Document Parsing Node is typically used in combination with the following nodes:
- Text Segmentation Node: Split long parsed text into segments suitable for large model processing
- Vector Storage Node: Convert parsed document content into vectors and store them for subsequent similarity searches
- Large Model Call Node: Use large models to analyze, summarize, or Q&A the parsed content
- Code Node: Perform custom processing and conversion of parsing results
- Condition Node: Choose different processing paths based on different characteristics of parsing results