Message Reply Node
What is a Message Reply Node?
The Message Reply Node is a basic node used to send information to users. When used in conjunction with large model nodes, it can also achieve streaming reply effects. It supports multiple message types, including plain text, Markdown formatted text, and various attachments (images, audio, video, files), allowing flexible information exchange with users.
Image Description:
The Message Reply Node interface mainly consists of a message type selection area and a content editing area. At the top, you can select the message type to send (text, Markdown, image, etc.), and the content editing area below will display corresponding configuration options based on the selected type, such as text editing boxes or attachment link input fields. Here you can configure the specific content to send to users.
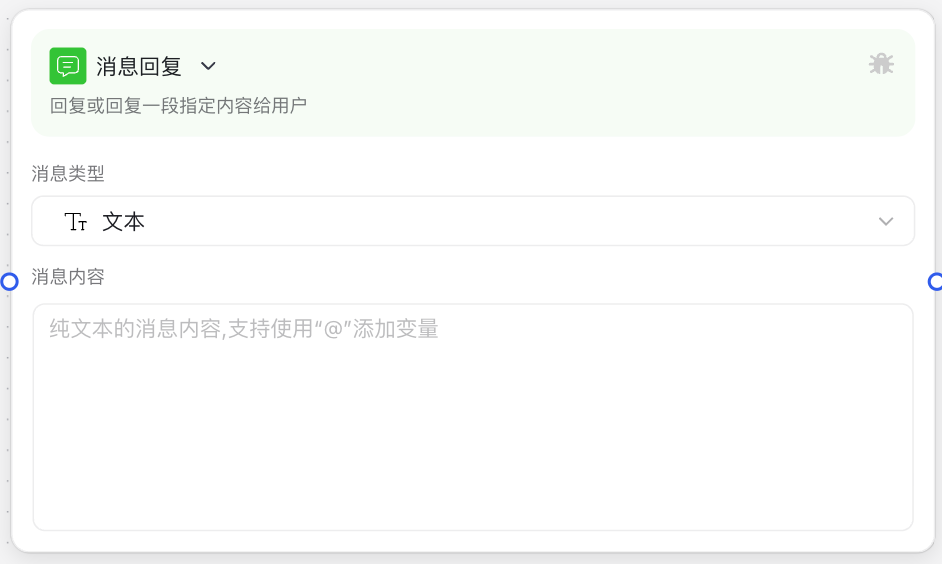
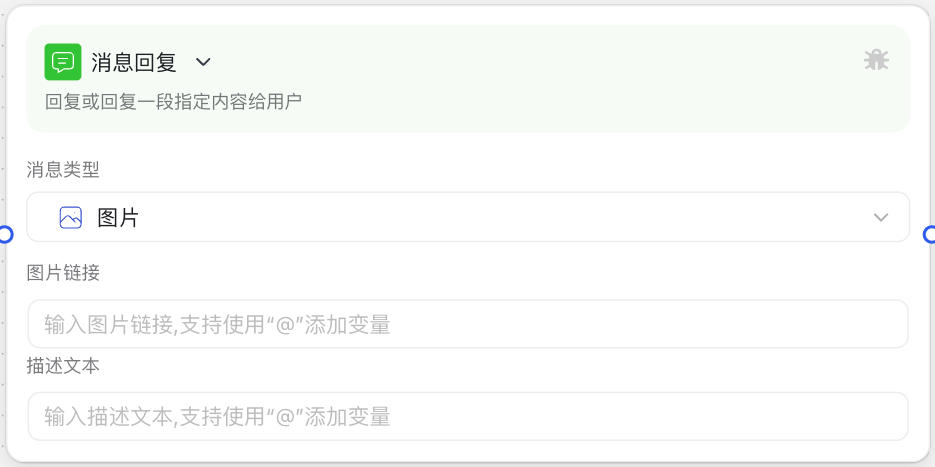
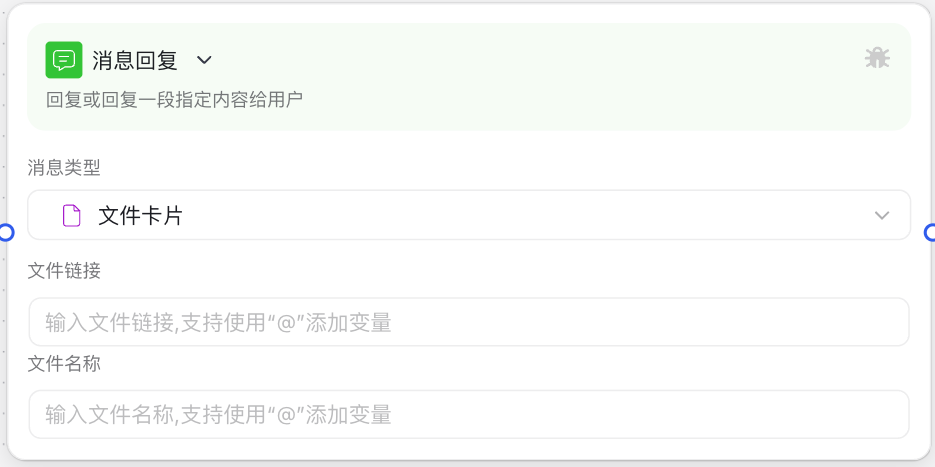
Why Do We Need a Message Reply Node?
When building intelligent workflows, the Message Reply Node solves the following key problems:
- Information Transmission: Conveys workflow processing results, status, or prompt information to users, maintaining interaction continuity.
- Diversified Expression: Through support for multiple message types (text, Markdown, attachments, etc.), makes reply content more diverse and enhances user experience.
- Structured Display: Uses Markdown format to create rich text effects like tables, lists, bold, italic, etc., making information more organized and easier to understand.
- Professional Content Sharing: Shares professional content like images and documents through attachment functionality, meeting complex business scenario needs.
Application Scenarios
1. User Q&A Replies
When users ask questions to the AI assistant, the Message Reply Node can send accurate, detailed text answers, providing users with the information they need. This is the most basic and common application scenario.
2. Structured Data Display
When needing to display structured data like tables and lists to users, you can use Markdown format to write content, such as displaying query results, product lists, task lists, etc.
3. File and Document Sharing
When users need to obtain files and documents like images, they can be sent as attachments, such as sharing product manuals, technical documentation, spreadsheets, etc.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Data Type | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Message Type | Specifies the type of message to send | Selector | Yes | Text |
| Content | Specific text content of the message | String | Depends on message type | None |
| Attachment Link | Access link for the attachment | String | Required for attachment types | None |
| Attachment Name | Display name for the attachment | String | Required for attachment types | None |
Message Type Description
The Message Reply Node supports the following message types:
- Text: Plain text messages, suitable for simple text replies
- Markdown: Formatted text supporting styles like headings, lists, tables
- Image: Sending image attachments
- Video: Sending video attachments
- Audio: Sending audio attachments
- File: Sending general file attachments
Input Description
The Message Reply Node's input mainly comes from the processing results of previous nodes in the workflow:
- Variable References: Can use
${variable_name}format in content fields to reference variables in the workflow - Dynamic Content: Supports referencing large model call results, conditional judgment results, etc.
- Attachment Paths: Can reference document parsing nodes, HTTP request nodes, etc. for generated attachment paths
Output Description
The Message Reply Node has no standard output content, depending on the message type set on the node
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Message Reply Node:
- Drag "Message Reply" node from the node panel to the canvas
- Connect the previous node to the Message Reply node
- Select Message Type:
- Click the node, select the message type to send in the right property panel
- Choose appropriate type based on business needs (text, Markdown, image, etc.)
- Configure Message Content:
- For text and Markdown types: Enter text to send in the "Content" field
- For attachment types (image, audio, video, file):
- Enter attachment URL in "Attachment Link" field
- Enter attachment display name in "Attachment Name" field
- Use Variable References:
- Use
${variable_name}format in content fields to reference workflow variables - Example:
Hello, ${user_name}! Your query result is: ${query_result}
- Use
- Save and Connect Next Node:
- Save configuration and connect to next node as needed
- If it's the last step of the process, can connect to end node
Advanced Techniques
Markdown Formatting Tips
Using Markdown format can make your messages more structured and beautiful:
- Heading Levels: Use
#,##,###to create different level headings - List Formats: Use
-or1.to create unordered or ordered lists - Table Creation: Use
|and-combination to create table structures - Text Emphasis: Use
**text**for bold or*text*for italic - Link Insertion: Use
[link text](URL)format to insert links
Example Markdown content:
## Query Results
Your query results are as follows:
| Item | Status | Completion |
|-----|------|-------|
| Task A | In Progress | 75% |
| Task B | Completed | 100% |
Please click [here](https://example.com) to view detailed report.Dynamic Content Generation
Combining with other nodes can generate more dynamic and personalized reply content:
- Combine with Large Model Calls: Reference content generated by large models for intelligent replies
- Combine with Conditional Branches: Dynamically determine reply content based on different conditions
- Combine with Code Execution: Use code to process data and generate formatted content
- Combine with HTTP Requests: Display data obtained from external APIs
Notes
Content Length Limits
- Text Length: Single message text content should not be too long, recommended to keep within 5000 characters
- Segmented Sending: For very long content, consider using multiple Message Reply nodes to send in segments
- Avoid Spamming: Don't send large numbers of messages in short time periods, may affect user experience
Attachment Usage Guidelines
- File Size: Attachments should be moderate in size, overly large files may cause slow loading
- Link Validity: Ensure attachment links are valid and have sufficient access permissions
- File Format: Ensure sent files are in common, easily opened formats
- Naming Convention: Attachment names should be concise and clear, expressing file content
Variable Reference Notes
- Variable Existence: Ensure referenced variables are defined and have values in the workflow
- Variable Type: Pay attention to variable data types, non-string types may need conversion
- Null Value Handling: Consider cases where variables may be null, set default values when necessary
- Escape Characters: Use backslash to escape
${}characters if needed in text
Common Issues
Why isn't my Markdown format displaying correctly?
- Syntax Error: Check if Markdown syntax is correct, especially for structures like tables and lists
- Client Support: Confirm if target client fully supports Markdown format
- Special Characters: Some special characters may need escaping, like
*,_,# - Empty Line Handling: Ensure paragraphs have empty lines between them, list items don't have empty lines
How to insert dynamically generated images in replies?
- Use HTTP Request Node: Get or generate images, obtain image URL
- Store URL in Variable: Store image URL in a variable
- Switch to Image Type: Select "Image" type in Message Reply node
- Reference URL Variable: Reference URL variable in attachment link field
How to handle message sending failures?
- Add Error Handling: Add conditional branch after Message Reply node to check sending status
- Set Retry Mechanism: Consider adding retry logic for important messages
- Log Errors: Use code execution node to record failure reasons
- Alternative Notification Channels: Configure alternative notification methods to ensure information delivery