Spreadsheet Parsing Node
Node Introduction
The Spreadsheet Parsing Node is a specialized tool for extracting and parsing Excel spreadsheet file content. Unlike ordinary document parsing nodes, the Spreadsheet Parsing Node can recognize the structure of tables, preserving key information such as worksheets, rows, and columns, allowing data to be used in a more structured (distinct from document parsing) way in the workflow. Without programming knowledge, you can easily obtain all the data in Excel spreadsheets with simple configuration, and save and transfer it according to the original structure of the table.
Image Description:
The Spreadsheet Parsing Node interface includes two main parts: input and output. The input section allows you to set the file source (file list, single file, etc.), while the output section is the parsed table data structure, including file information and table content. 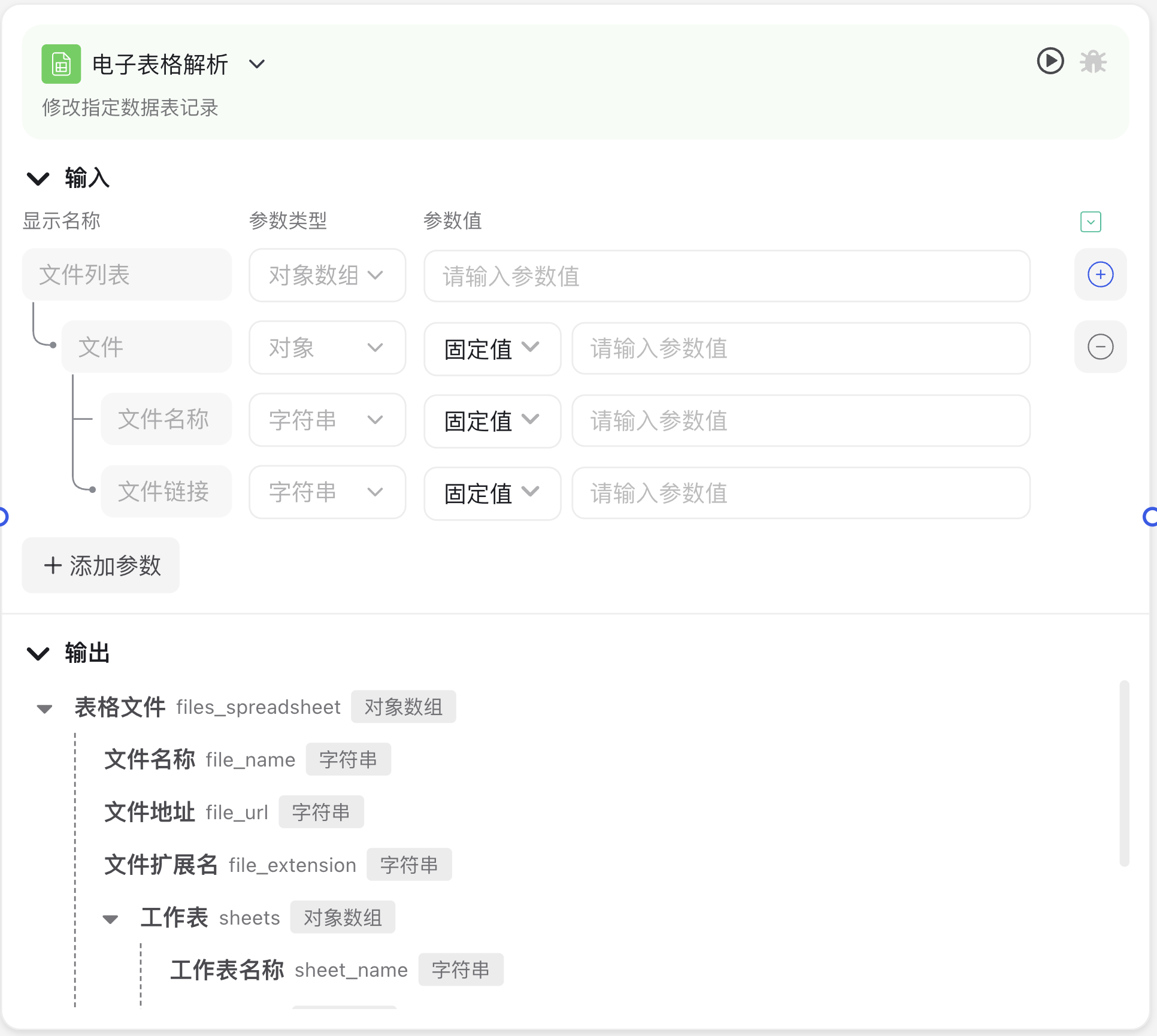
Why You Need the Spreadsheet Parsing Node
In daily work, Excel files are a common format for storing and transferring data. Through the Spreadsheet Parsing Node, you can:
- Automatic Content Acquisition: Automatically read data from Excel files, eliminating the tedious process of manual copy and paste
- Batch Processing: Process multiple spreadsheet files in batches, improving work efficiency
- Structured Analysis: Convert table data into structured formats for intelligent analysis and processing by subsequent nodes
- Intelligent Processing: Use large models to understand and operate on table data, achieving intelligent data processing
Application Scenarios
The Spreadsheet Parsing Node is suitable for the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: Data Analysis Automation:
Automatically read Excel files such as employee attendance sheets, sales reports, etc., analyze the data, and generate summary reports
Scenario 2: Data Import Processing:
Import spreadsheets such as product catalogs, customer information, etc., and store the data in systems or knowledge bases
Scenario 3: Intelligent Form Processing:
Parse Excel forms uploaded by users, perform data validation, cleaning, and conversion
Node Parameter Description
Input Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| File List | Select the list of Excel files to be parsed, which can be a collection of files passed from the previous node | Required | None |
| File | Single spreadsheet file object, choose one between this and File List | Conditionally Required | None |
| File Name | The name of the spreadsheet, usually used in conjunction with the file link | Conditionally Required | None |
| File Link | Download link or access path of the spreadsheet | Conditionally Required | None |
Output Parameters
The Spreadsheet Parsing Node outputs a structured table file object, including the following information:
| Output Content | Description |
|---|---|
| Table File (files_spreadsheet) | The spreadsheet file |
| File Name (file_name) | The name of the file |
| File URL (file_url) | The access address of the spreadsheet |
| File Extension (file_extension) | File format extension, such as xlsx, xls, etc. |
| Worksheet (sheet) | Contains worksheet data from the spreadsheet |
| Worksheet Name (sheet_name) | The name of the worksheet |
| Rows (rows) | Collection of row data in the worksheet |
| Row Index (row_index) | The row number, starting from 0 |
| Cells (cells) | Collection of cell data in the row |
| Value (value) | The actual value of the cell |
| Column Index (column_index) | The column number where the cell is located |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Node: Drag the "Spreadsheet Parsing" node from the node panel to the workflow canvas
- Connect Preceding Node: Connect the output of the preceding node (such as "Start Node" or "File Upload Node", etc.) to the Spreadsheet Parsing Node
- Set Input Parameters:
- If the preceding node provides a file list, select the "File List" parameter and reference the corresponding variable
- If you need to parse a specific file, fill in the "File Name" and "File Link" parameters
- Save Configuration: Click the save button to confirm the node settings
- Connect Subsequent Nodes: Connect the output of the Spreadsheet Parsing Node to downstream nodes (such as "Large Model Call" or "Code Execution", etc.)
Advanced Techniques
- Batch Process Multiple Tables:
- Configure a loop node to iterate through each spreadsheet in the file list
- Use the Spreadsheet Parsing Node to process individual files within the loop
- Use the Variable Saving Node to store processing results
- Table Data Conversion:
- Combined with the Code Execution Node, you can convert the parsed table data to different formats
- For example, convert table data to JSON format or CSV format
- Intelligent Table Understanding:
- Pass the parsed table data to the Large Model Call Node
- Use prompts to guide the large model to understand the table structure and data meaning
- Have the large model generate summaries of the table data or answer related questions
Precautions
File Format Support
- Supported file formats include:
.xlsx,.xls,.csv - For other formats of table files, it may be necessary to convert them to the above formats before parsing
- Particularly complex Excel spreadsheets (such as those containing macros, charts, etc.) may affect parsing results
Data Volume Limitations
- For very large tables (such as data with hundreds of thousands of rows), the parsing process may take a long time
- It is recommended to process large tables in chunks, or to filter out the required data parts before parsing
- If performance issues are encountered, consider using the Code Execution Node for optimized processing
Encoding and Language
- For tables containing special characters or multilingual content, please ensure the file uses UTF-8 encoding
- Non-English characters such as Chinese may need additional processing to display correctly after parsing
Frequently Asked Questions
Empty Parsing Results
Problem: Configured the Spreadsheet Parsing Node, but the output result is empty or has no data.
Solution:
- Check if the input file is valid and if the file link is accessible
- Confirm that the Excel file actually contains data, not an empty table
- Check if the file format is supported; older Excel formats may need conversion
- Try downloading the file locally first, then uploading it to the platform for processing
Incomplete Parsing Data
Problem: Only part of the table data is parsed, some content is lost or incorrect.
Solution:
- Check if the original table has merged cells, which may affect parsing results
- Confirm if the table contains special formats (such as formulas, charts, etc.), which may not be fully parsed
- For Excel files with multiple worksheets, ensure you are focusing on the correct worksheet
- Try converting the Excel to a simple format (such as CSV) before parsing
Unable to Recognize Date Formats
Problem: Dates in the table become numbers or other formats after parsing.
Solution:
- Explicitly set the date column format to date format in Excel
- Use the Code Execution Node to convert date formats after parsing
- Use the Large Model Call Node to recognize and convert date formats