Tool Node
What is a Tool Node?
The Tool Node is a powerful node in Magic Flow that allows you to call and use various preset tools within workflows. Like a multi-functional Swiss Army knife, the Tool Node helps you execute specific tasks such as data processing, information queries, or automated operations. You can use these tools in two ways: through natural language descriptions (large model calls) or direct parameter settings (parameter calls), meeting different scenario requirements.
Image Description:
The Tool Node interface mainly consists of a call mode selection area and a parameter configuration area. At the top, you can choose between "Large Model Call" or "Parameter Call" modes, while below is the system's custom input parameter configuration area, supporting the addition of multiple parameters and their expressions. 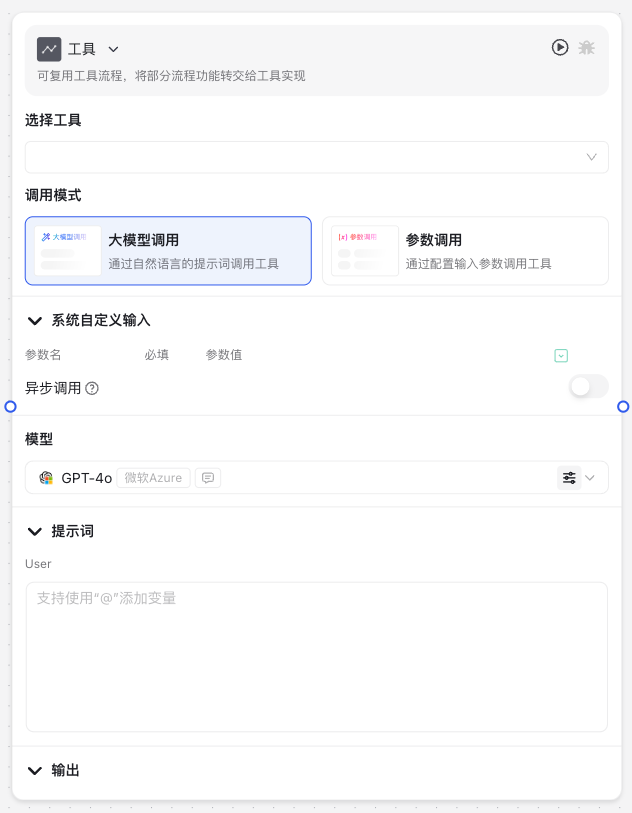
Why Do We Need a Tool Node?
When building intelligent workflows, you often need to execute standardized tasks or call specific functions. The Tool Node exists to solve this problem:
- Function Extension: Expands Magic Flow's capabilities, enabling workflows to perform more specialized tasks
- Standardized Operations: Provides a unified interface for calling various tools, simplifying workflow design
- Flexible Calls: Supports multiple calling methods, making it easy to use even without technical background
- Process Automation: Converts manual operations into automated processes, improving efficiency and consistency
Application Scenarios
The Tool Node is suitable for various scenarios, including but not limited to:
- Information Queries: Calling search tools to obtain real-time information or professional knowledge
- Data Processing: Using data transformation tools to process and format workflow data
- Automated Operations: Triggering automated tasks such as sending notifications or creating schedules
- Intelligent Assistant Enhancement: Adding practical tool capabilities to chatbots, such as weather queries or text translation
Node Parameter Description
Input Description
The Tool Node's input parameters are mainly divided into two categories: call mode settings and tool parameter configuration.
| Parameter Name | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Call Mode | Select tool calling method, including [Large Model Call] and [Parameter Call] | Yes | Large Model Call |
| Select Tool | Choose the tool name to use | Yes | None |
| Model | When using [Large Model Call], select the model to use | Yes | GPT-4o |
| Prompt | Use prompts to guide the large model, ensuring accurate usage, supports using variables with @ | No | None |
Output Description
After Tool Node execution, it outputs the following:
| Output Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Output Text | Result text from tool execution | "Current Beijing weather: Sunny, 25°C" |
| Execution Status | Tool execution status, success or failure | "success" |
| Error Message | If execution fails, contains error details | "API call timeout" |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Tool Node
- Drag "Tool" node from node panel to workflow canvas
- Connect node with other nodes in workflow
- Select Call Mode
- Choose "Large Model Call" or "Parameter Call" in node configuration panel
- Large Model Call: Suitable for using tools through natural language descriptions
- Parameter Call: Suitable for using tools through direct parameter configuration
- Configure Parameters
- Click "Add" button to add parameters required by tool
- Fill in parameter name, set whether required
- Select appropriate expression type (such as text, number, etc.)
- Fill in parameter value or expression
- Set Nested Parameters (if needed)
- For complex tools, click "+" button next to parameter to add sub-parameters
- Configure sub-parameters in same way
- Configure Output
- Select output format in "Output" section (default is text)
- Enable or disable certain output items as needed
Advanced Techniques
- Using Variable References
- Check "Use @flow variables" option to use @ symbol to reference workflow variables in parameter values
- Example: Enter "@user_question" in parameter value to use "user_question" variable value from workflow
- Dynamic Parameter Calculation
- Can use simple calculation formulas in expressions
- Example: "NaN" will automatically calculate result of count variable value plus 1
- Using Tool Results in Conditional Judgments
- Tool Node output can be used as input for conditional branch nodes
- Can choose different process branches based on tool execution results
Notes
Parameter Configuration Notes
- Parameter Naming Conventions
- Parameter names should be concise and clear, reflecting parameter purpose
- Avoid spaces and special characters, recommend using English letters, numbers, and underscores
- Required Parameter Handling
- All parameters marked as "required" must have valid values configured
- If required parameters have no values, tool cannot execute normally
- Parameter Value Format
- Ensure parameter values conform to tool's required format
- Special type data like dates and numbers need to be provided in specified format
Performance and Limitations
- Execution Timeout
- Tool calls have default timeout limit (usually 30 seconds)
- Long-running tools may fail due to timeout
- Call Frequency
- Some tools may have call frequency limits
- Avoid frequently calling same tool in short time period
Common Issues
Issue 1: What to do when Tool Node execution fails?
Solution: When Tool Node execution fails, you can troubleshoot through following steps:
- Check if all required parameters are correctly configured
- View error message to understand specific failure reason
- Confirm parameter format is correct, especially for special formats like dates and JSON
- Check if network connection is normal (for tools requiring network access)
- If using variable references, confirm variable exists and has value
Issue 2: How to choose between Large Model Call and Parameter Call?
Solution: Suggestions for choosing call mode:
- Large Model Call: Suitable for scenarios requiring natural language understanding, such as when you want to use tools through descriptive language, or when tool input parameters are complex
- Parameter Call: Suitable for scenarios with clear, fixed parameters, can obtain more stable, predictable results, suitable for process-oriented, standardized tasks
Common Node Combinations
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Large Model Call Node | Tool Node can serve as extension capability for large models, handling professional tasks |
| Conditional Branch Node | Determine subsequent process direction based on tool execution results |
| Message Reply Node | Display tool execution results as reply content to users |
| Variable Save Node | Save tool execution results for use by subsequent nodes |