Loop Node
What is a Loop Node?
The Loop Node is a flow control node in Magic Flow workflow that allows you to repeatedly execute a series of operations until a specific condition is met or a specified number of iterations is completed. Simply put, the Loop Node acts like a "repeat execution" instruction, helping you automate repetitive tasks and improve work efficiency.
Image Description: The Loop Node interface includes two main parts: the outer "Loop" component and the inner "Start Node". In the Loop component, you can set the loop type, loop conditions, or count; the Start Node represents the starting point of each loop iteration. 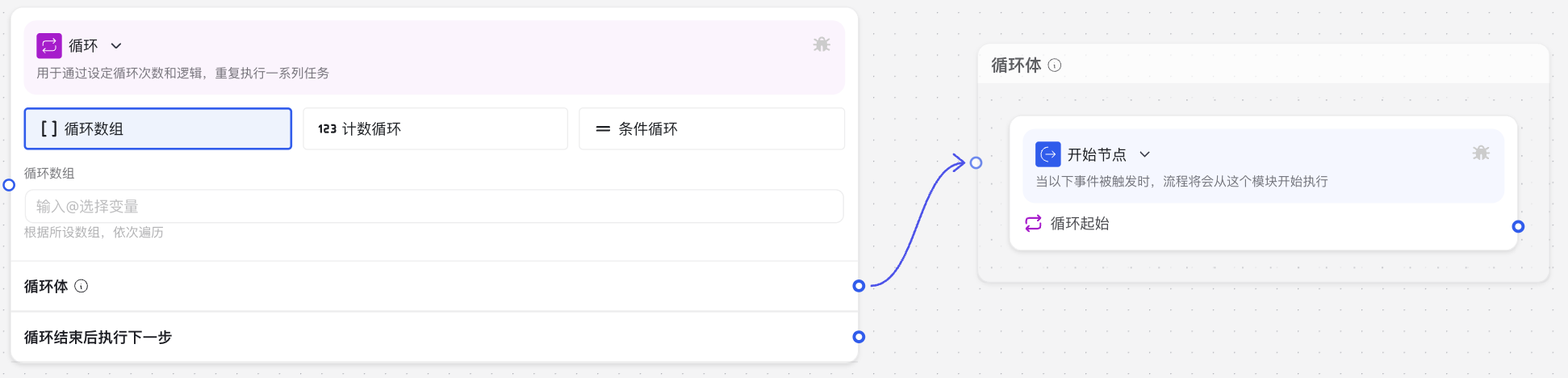
Why Do We Need Loop Node?
In building intelligent applications, the Loop Node solves the problem of needing to repeat certain operations, it can:
- Batch Process Data: Perform the same operation on each element in a list or array
- Retry Attempts: Continue executing a task until specific conditions are met
- Timed Execution: Repeat tasks a fixed number of times
- Dynamic Workflow: Flexibly decide execution count based on actual situations
- Save Work: Avoid manually copying and pasting the same node sequence
Application Scenarios
1. Batch Data Processing
Process a set of data, such as sending personalized messages to a customer list or processing each row in a table.
2. Retry Mechanism
Retry when certain operations fail, until success or maximum attempt count is reached.
3. Paginated Requests
When multiple API calls are needed to get paginated data, control request count and parameter changes through loops.
4. Periodic Checking
Repeatedly check a status according to set count or conditions, such as regularly checking task completion status.
Node Parameter Description
Basic Parameters
| Parameter Name | Parameter Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loop Type | Dropdown | Yes | Select loop type, including "Count Loop", "Array Loop", and "Condition Loop" |
| Loop Count | Number/Variable | Depends on type | When "Count Loop" is selected, set total number of loop executions |
| Loop Array | Variable | Depends on type | When "Array Loop" is selected, specify array or list to iterate over |
| Loop Condition | Expression | Depends on type | When "Condition Loop" is selected, set condition expression for loop continuation |
| Current Index Variable Name | Text | No | Variable name to store current loop index, defaults to "loopIndex" |
| Current Element Variable Name | Text | No | Variable name to store current loop element, defaults to "loopItem" |
| Maximum Loop Count | Number | No | Safety limit to prevent infinite loops, set maximum executable loop count |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Choose Loop Type:
- By Count: Suitable when exact execution count is known
- Array Iteration: Suitable when needing to process each array element
- Condition Check: Suitable when needing to stop only when specific conditions are met
- Configure Loop Parameters:
- By Count: Set specific loop count, like "10"
- Array Iteration: Select or input array variable to iterate over
- Condition Check: Set loop condition expression and maximum loop count
- Configure Loop Body:
- Add nodes that need to be repeatedly executed inside loop node
- These nodes will execute repeatedly according to loop settings
- Handle Loop Results:
- Can use variable save node to save intermediate results within loop
- After loop ends, these variables are available for subsequent nodes
Important Notes
Performance Considerations
Loop nodes may extend workflow execution time:
- Avoid setting too large loop counts
- Consider batch processing for large amounts of data
- Always set reasonable maximum loop count for condition loops to prevent infinite loops
Variable Scope in Loops
Variables modified in loops affect subsequent iterations:
- If independent variables needed for each loop, reinitialize at loop start
- Variable modifications in loop persist until loop ends
Loop Nesting Limitations
While technically supporting nested loops, note:
- Nested loops significantly increase execution complexity and time
- Recommend no more than 2 levels of nesting to maintain workflow maintainability
- Pay special attention to setting reasonable loop counts when nesting loops
Common Issues
Issue 1: What If Loop Node Executes More Times Than Expected?
Solutions: Loop conditions might be improperly set. Recommend:
- Check if loop conditions are correctly set
- Ensure condition judgment variables are updated at appropriate times
- Use code node to manually set break flags to end loop early
Issue 2: What If Nodes Inside Loop Don't Execute as Expected?
Solutions: This might have several causes:
- Ensure nodes inside loop body are correctly connected
- Check if condition judgments for each node are correct
- Use variable save node to save intermediate results for debugging
- Check if variables used in loop are correctly initialized
Issue 3: How to Save Results from Each Iteration in Loop?
Solutions: You can:
- Use array variables to collect results from each loop
- Add results to array in code execution node
- After loop ends, array will contain results from all iterations
// Initialize results array (before loop)
context.variableSave("results", []);
// Save each result inside loop
let results = context.variableGet("results", []);
results.push(someResult);
context.variableSave("results", results);Best Practices
Common Paired Nodes
| Node Type | Pairing Reason |
|---|---|
| Code Execution Node | Handle complex logic in loops, operate on arrays and objects |
| Conditional Branch Node | Execute different operations in loop based on conditions |
| Variable Save Node | Store intermediate results or accumulated values in loop |
| HTTP Request Node | Send batch requests or get paginated data |
| Data Storage Node | Save loop processing results to persistent storage |