Wait Node
What is a Wait Node?
The Wait Node is a pause point in a workflow, used to wait for user reply messages before continuing the process. Like waiting for a response after asking a question in a conversation, the Wait Node pauses workflow execution until receiving a new user message or exceeding the set wait time. This allows you to design multi-turn interactive dialogue flows, implementing more complex human-machine interaction scenarios.
Image Description:
The Wait Node interface mainly consists of three parts: the top displays the "Wait" title, indicating the node is waiting for user reply; the middle section shows the output data the system will obtain, including session ID, topic ID, message content, etc.; the bottom area contains timeout settings, where you can enable and set the wait timeout duration. 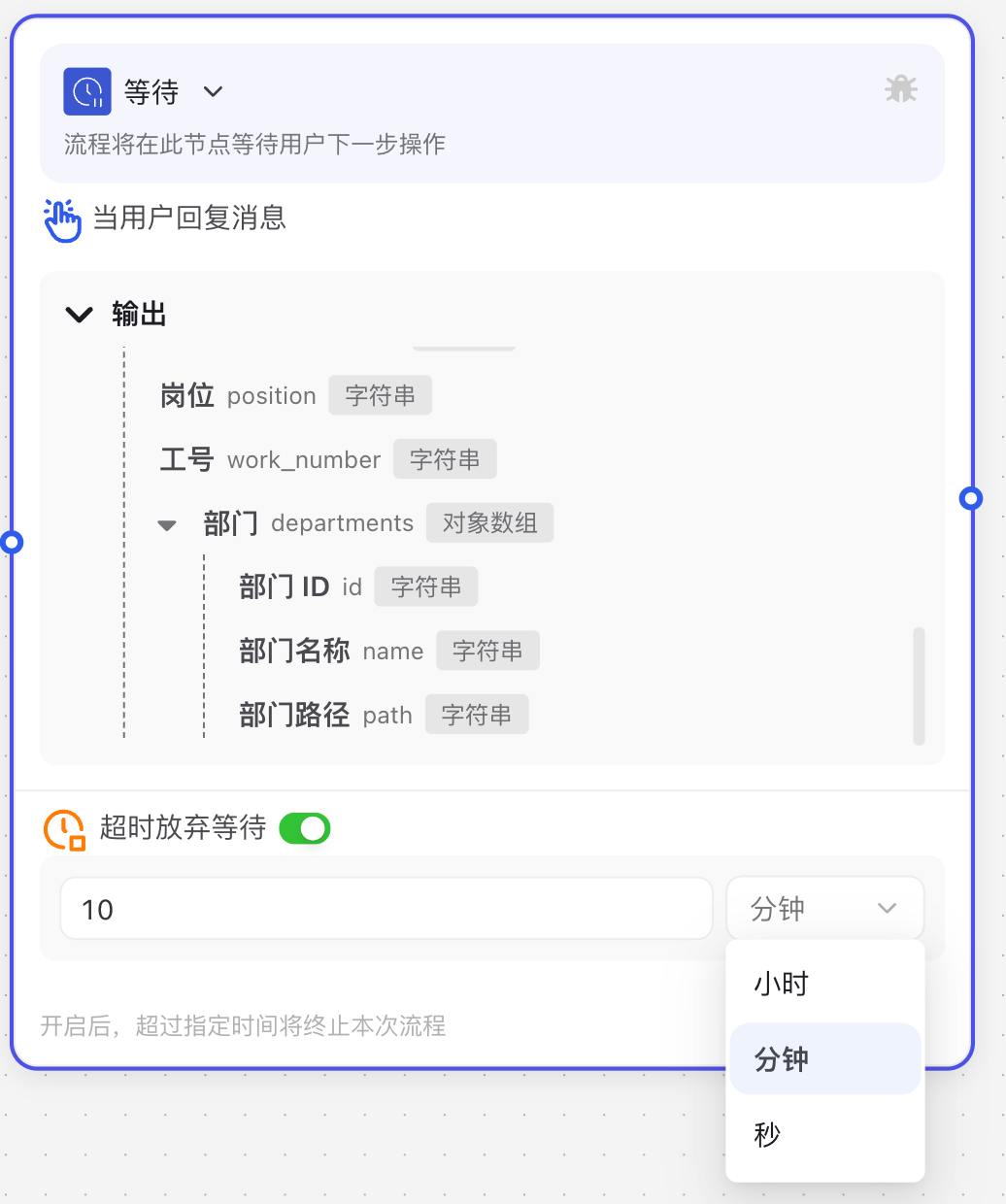
Why Do We Need a Wait Node?
When building interactive workflows, the Wait Node solves the following key problems:
- Create Multi-turn Dialogues: The Wait Node allows you to design dialogue flows requiring multiple user inputs, making conversations more natural and coherent.
- Collect User Confirmation or Additional Information: When the process needs user confirmation or additional information, the Wait Node can pause the process and wait for user response.
- Control Conversation Flow: The Wait Node lets you precisely control conversation rhythm and flow, avoiding poor user experience from continuous bot messages.
- Handle Timeout Situations: Through timeout settings, you can handle cases where users don't reply for long periods, ensuring the process doesn't wait indefinitely.
Application Scenarios
1. Form Filling
Guide users through form completion step by step, with each Wait Node corresponding to a form field input. The system can validate after user input and guide to the next step.
2. Multi-step Confirmation Process
Before executing important operations, use Wait Nodes to design multi-step confirmation processes, ensuring users understand and agree to operation consequences.
3. Information Collection and Clarification
When user's initial question isn't clear enough, use Wait Nodes to request more details or clarification, then provide more accurate answers based on complete information.
Node Parameter Description
Input Description
The Wait Node has no special input parameters, it mainly focuses on obtaining information from the next user message.
Output Parameters
After waiting for user reply, the node will output the following parameters:
| Parameter Name | Description | Data Type | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Session ID | Unique session identifier for user-AI assistant interaction | String | Used for associating dialogue context |
| Topic ID | Identifier for current conversation topic | String | Used for distinguishing different topics within same session |
| Message Content | Text message sent by user | String | Main content for workflow processing |
| Message Type | Message type identifier | String | Such as text, image, etc. |
| Send Time | Message timestamp | String | Records message time information |
| Organization Code | Code of user's organization | String | Used for organization-level functions and permission management |
| File List (files) | File list information and basic identifiers | Object Array | |
| User (user) | Basic user information | Object |
File List Parameters
When user reply contains files, you can access file-related information:
| Parameter Name | Description | Data Type | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Name | Original name of uploaded file | String | Used for displaying and processing files |
| File Link | URL for accessing the file | String | Used for downloading or accessing file content |
| File Extension | File format suffix | String | Such as pdf, docx, xlsx, etc. |
| File Size | File size in bytes | Number | Used for file processing control |
User Information Parameters
Basic information of current interacting user provided by system:
| Parameter Name | Description | Data Type | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| User ID | Unique user identifier | String | Used for user identification and data association |
| User Nickname | User's display name | String | Used for personalized interaction |
| Real Name | User's actual name | String | Used for formal addressing |
Timeout Setting Parameters
Used to control maximum wait time:
| Parameter Name | Description | Data Type | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable Timeout | Whether to enable timeout function | Boolean | When enabled, will automatically end wait after exceeding set time |
| Timeout Duration | Maximum wait time | Number | Set specific time value |
| Time Unit | Unit for timeout duration | String | Can choose seconds, minutes, or hours |
Usage Instructions
Basic Configuration Steps
- Add Wait Node:
- Drag "Wait" node from node panel to canvas
- Connect it to previous node (usually message reply node)
- Set Timeout Options (Optional):
- Enable "Timeout Abandon Wait" option
- Set timeout duration (e.g., 10)
- Select time unit (e.g., minutes)
- Connect Next Node:
- Drag connection line from Wait Node to next processing node
- Ensure workflow has clear processing path after receiving user reply
- Configure Timeout Branch (if timeout enabled):
- Create independent processing branch for timeout situation
- Or simply end process for timeout situation
Advanced Techniques
Using Variables to Save Wait Node Output
- Add Variable Save Node: Add variable save node after Wait Node
- Save User Reply: Save Wait Node's "Message Content" as variable
- Reference Saved Variable: Reference this variable in subsequent nodes to process user reply
Designing Different Timeout Handling Strategies
- Friendly Reminder: Send reminder message after timeout, then end process
- Default Value Handling: Use default value to continue process after timeout
- Re-ask: Re-ask question after timeout, giving user second chance
Notes
Clear Prompt Information
- Specific Instructions: In message reply before Wait Node, clearly tell users what information they need to provide
- Format Requirements: If there are specific format requirements for user reply, clearly state them
- Expected Reply Type: Clearly inform users whether they need to reply with text, options, or upload files
Reasonable Timeout Settings
- Based on Question Complexity: Complex questions need longer wait times
- Consider User Scenario: Understand user environment, mobile users may need longer response time
- Avoid Too Short Timeout: Too short timeout may cause timeout before user can reply
Handling Unexpected Input
- Input Validation: Add condition node after Wait Node to validate if user input meets expectations
- Error Handling: Provide clear error messages for unexpected input and possibly request re-input
- Compatible with Multiple Expressions: Consider cases where users may express same meaning in different ways
Common Issues
How to determine if user reply is valid content?
- Use Conditional Branch Node: Add conditional branch node after Wait Node
- Set Validation Conditions: Such as checking if message content is empty, contains specific keywords
- Separate Processing: Process valid and invalid replies through different branches
What to do if receiving file instead of text after Wait Node?
- Check Message Type: Use conditional branch node to check "Message Type" parameter
- File Processing Path: When message type is file, follow specific processing branch
- File Validation: Check if file extension, size, etc. meet expectations
- Prompt Re-upload: If file doesn't meet requirements, guide user to re-upload
How to handle multiple user replies?
Wait Node will only capture and process the first reply message from user. To handle multiple replies:
- Chain Multiple Wait Nodes: Design multiple consecutive Wait Nodes, each processing one reply
- Use History Message Query: Query user history messages when needed to get multiple replies
- Clear Guidance: Clearly inform users in process that they need to provide all information in single message
Common Node Combinations
- Message Reply Node: Send prompt information before waiting, telling users what they need to provide
- Conditional Branch Node: Process user reply, determine if it meets expectations
- Large Model Call Node: Analyze user reply content, generate corresponding response
- Variable Save Node: Save user reply for use in subsequent process
| Node Type | Combination Reason |
|---|---|
| Message Reply Node | Send prompt information before waiting, telling users what they need to provide |
| Conditional Branch Node | Process user reply, determine if it meets expectations |
| Large Model Call Node | Analyze user reply content, generate corresponding response |
| Variable Save Node | Save user reply for use in subsequent process |